Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Psychiatr. Jul 19, 2020; 10(7): 150-161
Published online Jul 19, 2020. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v10.i7.150
Published online Jul 19, 2020. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v10.i7.150
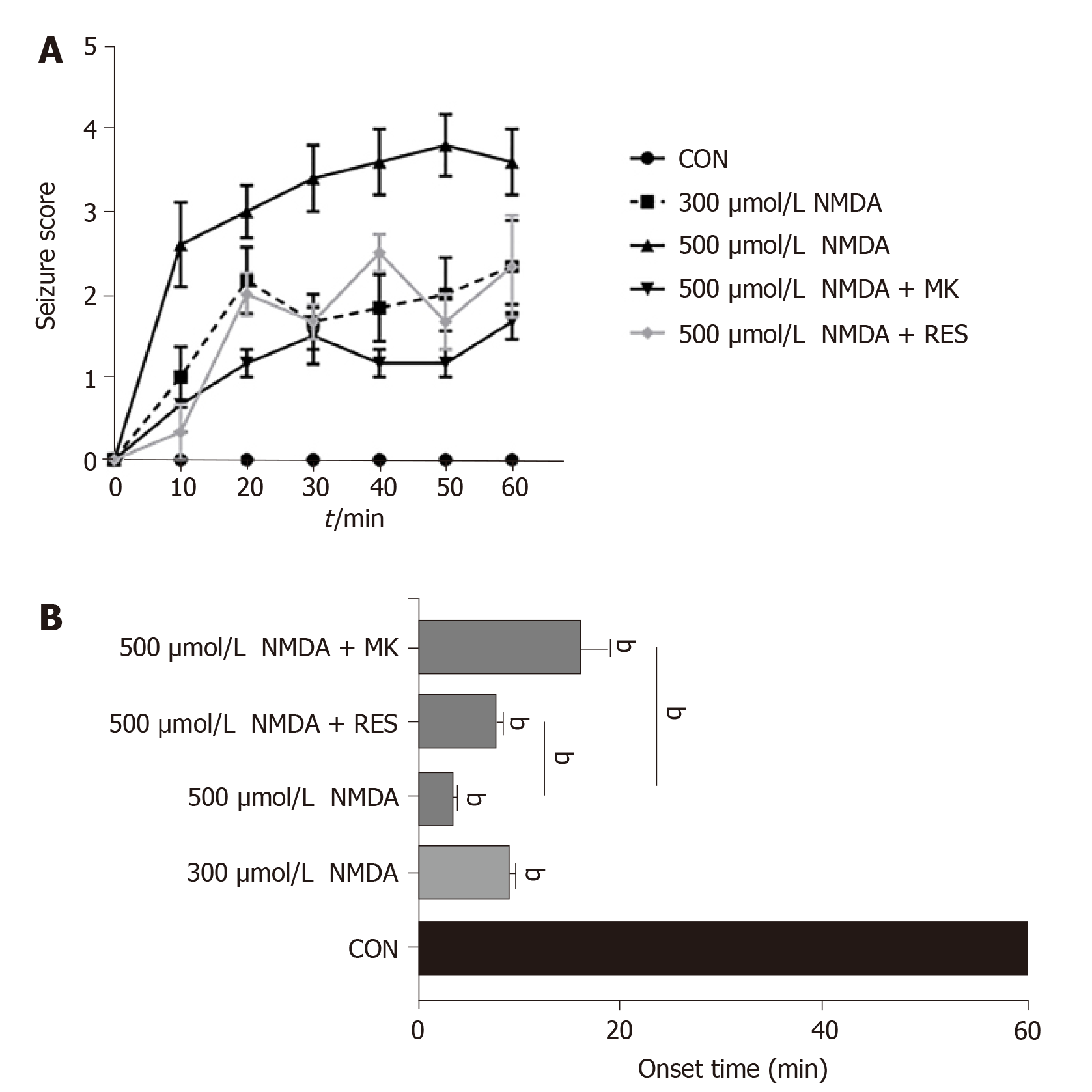
Figure 4 Immersion of N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid causes persistent seizure-like behavior in zebrafish.
Seizure activity scores and onset times following N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA)-immersion (300 μmol/L and 500 μmol/L NMDA, 40 mg/L resveratrol + 500 μmol/L NMDA, and 3 mg/kg MK-801 + 500 μmol/L NMDA). A: The mean seizure scores (± SE) for each group plotted against time after NMDA immersion; B: The latency of seizure onset after NMDA immersion. Bars represent mean ± SE of the time lag to the onset of the first convulsion in each group. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and t-test for the different groups (n = 6) (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control). NMDA: N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid; RES: Resveratrol; MK: MK-801.
- Citation: Long XY, Wang S, Luo ZW, Zhang X, Xu H. Comparison of three administration modes for establishing a zebrafish seizure model induced by N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid. World J Psychiatr 2020; 10(7): 150-161
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v10/i7/150.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v10.i7.150