Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Exp Med. Feb 20, 2017; 7(1): 11-24
Published online Feb 20, 2017. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v7.i1.11
Published online Feb 20, 2017. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v7.i1.11
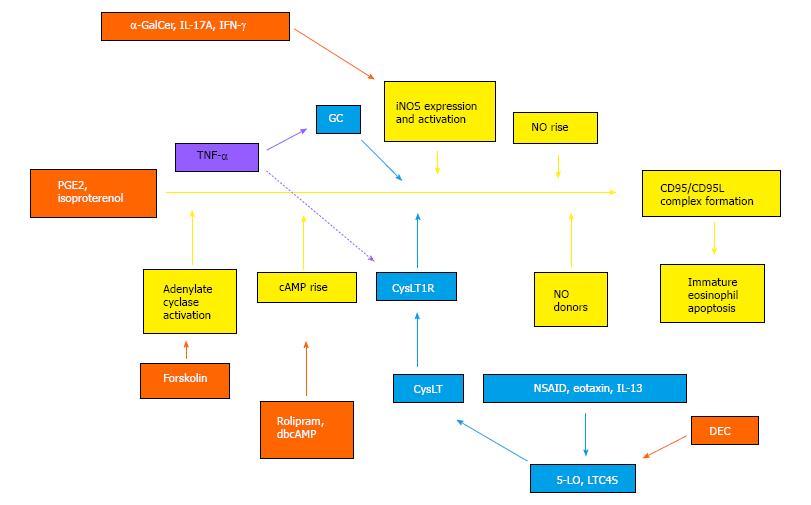
Figure 2 A graphical abstract of the main events identified in extrinsic regulation of bone-marrow eosinopoiesis, and of the hypothetical interactions of tumor necrosis factor-α with the underlying mechanisms.
Colored boxes and arrows identify different classes of agents and their actions as follows: Orange, extrinsic suppressors of murine bone-marrow eosinopoiesis both in vitro[23,26,72,73] and in vivo[47,54]; light blue, extrinsic enhancers of eosinopoiesis in vitro[25,36,51,70] and in vivo[45,47,52,53]; yellow, essential components of a proapototic sequence (iNOS-CD95L-dependent pathway[54,72,73]) which is susceptible to activation by the first (orange-labeled) and blockade by the second (light blue-labeled) sets of extrinsic regulators; lavender, TNF-α, presenting both constitutive (continuous arrow) and challenge-induced (discontinous arrow) effects, inside the bone-marrow, besides its extramedullary actions[45] as activator of the HPA axis (not shown). TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: Xavier-Elsas P, Masid-de-Brito D, Vieira BM, Gaspar-Elsas MIC. Odd couple: The unexpected partnership of glucocorticoid hormones and cysteinyl-leukotrienes in the extrinsic regulation of murine bone-marrow eosinopoiesis. World J Exp Med 2017; 7(1): 11-24
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v7/i1/11.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v7.i1.11