Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Crit Care Med. Jul 9, 2022; 11(4): 228-235
Published online Jul 9, 2022. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v11.i4.228
Published online Jul 9, 2022. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v11.i4.228
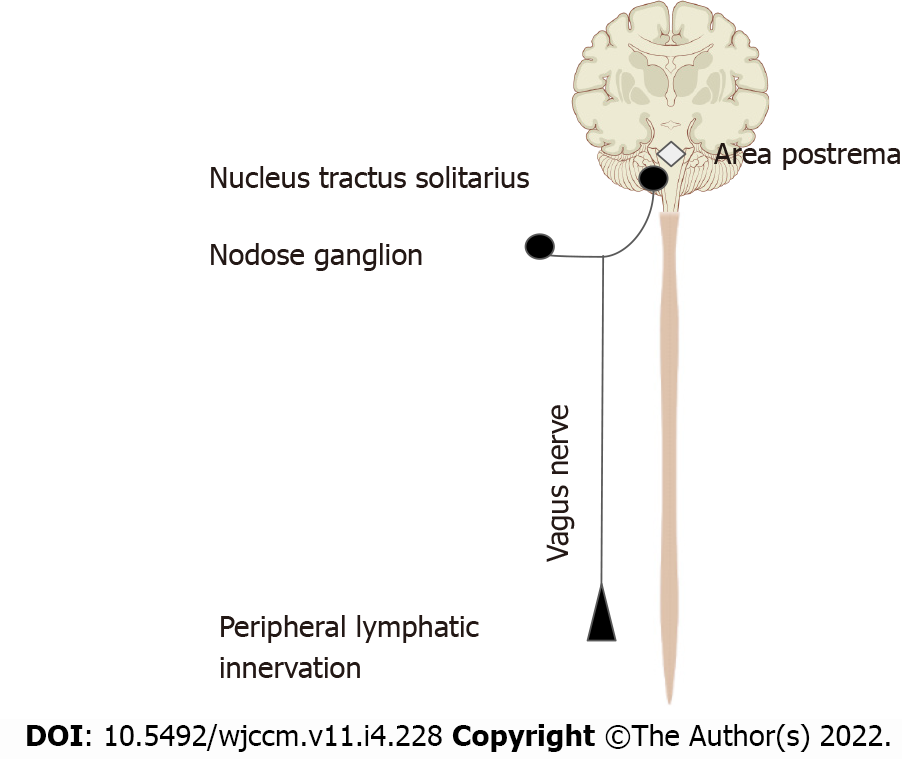
Figure 2 Afferent limb of the inflammatory reflex.
This figure demonstrates the mechanisms by which the vagus nerve senses inflammation. Vagal sensory neurons directly express receptors for various pro-inflammatory cytokines such as, tumor necrosis factor, interleukin 1β, neuropeptide Y and prostaglandins. Vagal fibers innervating the lymphatic system demonstrate sensitivity to interleukin-1β. In addition, the nodose ganglion has been shown to express Toll-like receptors. Area postrema directly expresses proinflammatory cytokine receptors[22]. The signal is transmitted via the vagal afferents to the bilateral nucleus tractus solitarius, the primary vagal afferent nucleus[19].
- Citation: Ahmad F. Medicinal nicotine in COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome, the new corticosteroid. World J Crit Care Med 2022; 11(4): 228-235
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v11/i4/228.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v11.i4.228