Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Immunol. Jul 27, 2016; 6(2): 105-118
Published online Jul 27, 2016. doi: 10.5411/wji.v6.i2.105
Published online Jul 27, 2016. doi: 10.5411/wji.v6.i2.105
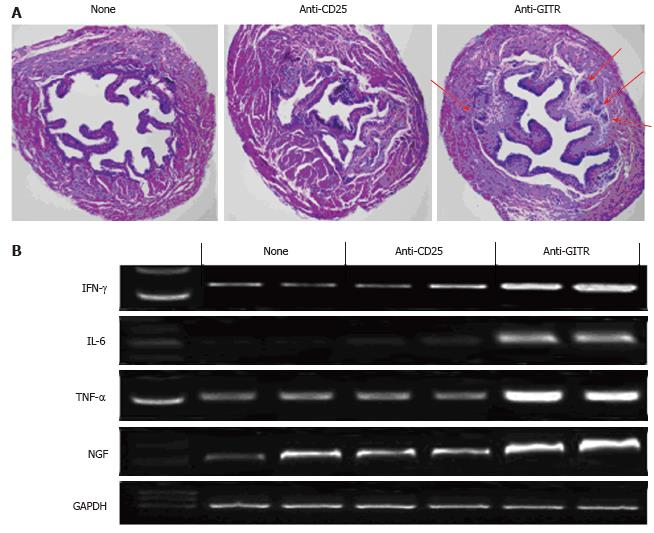
Figure 9 Depletion of CD4+ Treg cells results in bladder autoimmune inflammation in urothelium-ovalbuminGFP-Foxp3/OT-II mice.
URO-OVAGFP-Foxp3/OT-II mice were treated with anti-CD25 or anti-GITR mAb every other day beginning at 6 wk of age and sacrificed for analysis at 10 wk. A: Bladder histological H and E staining. The slides are representative of 12 bladders for each of anti-CD25 and anti-GITR mAb treated groups. Cellular infiltration is indicated by red arrows. The bladder of an untreated mouse is included for comparison. The summary of bladder histological inflammation is shown in Table 1; B: RT-PCR analysis of IFN-γ, IL-6, TNF-α and NGF mRNA expressions in the bladders of mice treated with anti-CD25 or anti-GITR mAb. GAPDH was used as an internal control. The bladders from untreated mice are included for comparison. UROGFP-Foxp3/OT-II: Urothelium-ovalbuminGFP-Foxp3/OT-II mice; RT-PCR: Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction; IFN: Interferon; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; NGF: Nerve growth factor.
- Citation: Liu WJ, Luo Y. Regulatory T cells suppress autoreactive CD4+ T cell response to bladder epithelial antigen. World J Immunol 2016; 6(2): 105-118
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2824/full/v6/i2/105.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5411/wji.v6.i2.105