Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Immunol. Nov 27, 2015; 5(3): 99-112
Published online Nov 27, 2015. doi: 10.5411/wji.v5.i3.99
Published online Nov 27, 2015. doi: 10.5411/wji.v5.i3.99
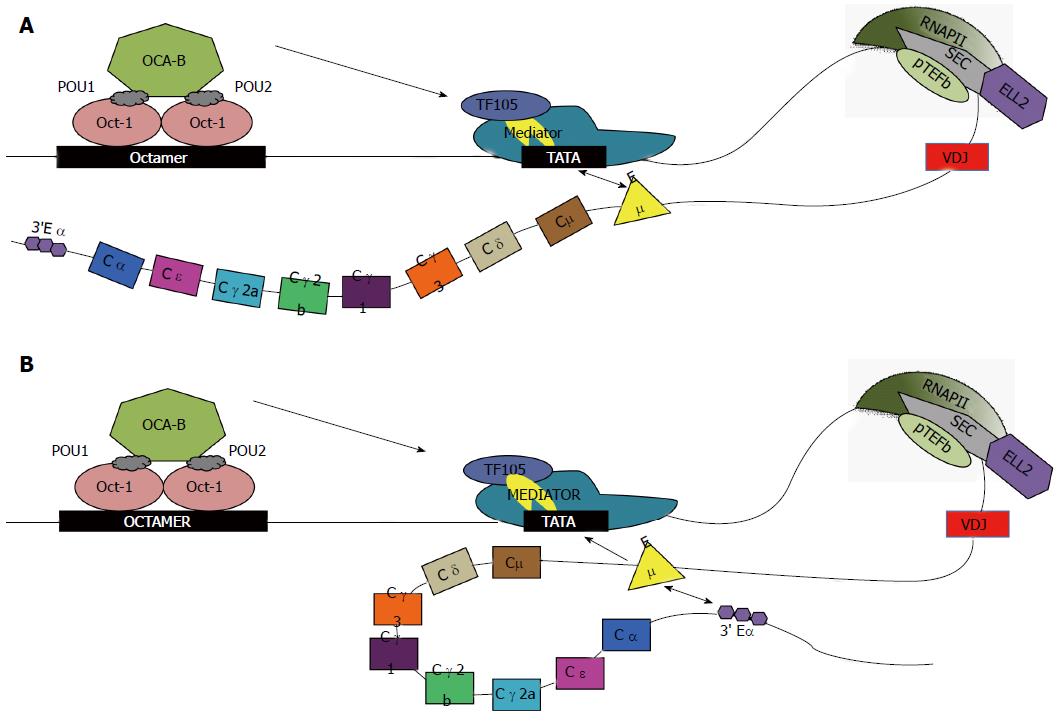
Figure 1 Transcription of Igh with alternative enhancer interactions.
Oct-1 and -2 bind to the octamer sequence; OCA-B binds to Oct-2 and with TF105 (purple oval), a TFIID variant that is part of the basal transcription complex including TBP (yellow). Mediator (large teal complex) is a large complex of proteins that facilitates binding of RNAP-II to INR. Factors in Mediator like cdk8/cyclin C phosphorylate RNAP-II at ser-5 in the CTD consensus 7-mer for initiation. Then P-TEFb (cyclinT and cdk9, green oval) phosphorylates the ser-2 position of the CTD repeats of RNAP-II. Many genes have stalled polymerases awaiting the SEC, which contains ELL2 (purple hexagon) and P-TEFb[60]. Phosphorylation of the CTD by ser-5 and ser-2 is high near the Igh promoter[61]. The other members of the SEC are shown in gray. Differential transcription elongation occurs due to the potential interaction of the Igh enhancers. Cμ enhancer (annotated Eμ) interacts with promoter of Igh. A: In the first case, classical transcription of Igh can occur due to interaction between the promoter and enhancer, depicted by double arrow, without large-scale chromosomal looping; B: In the second case, along with promoter-enhancer interactions, Cμ enhancer has been hypothesized to interact with the 3’ Cα enhancer (3’ Eα), causing chromosomal looping. CTD: Carboxyl-terminal domain; SEC: Super elongation complex; TBP: TATA-binding protein; P-TEFb: Positive elongation factor b.
- Citation: Smith SM, Carew NT, Milcarek C. RNA polymerases in plasma cells trav-ELL2 the beat of a different drum. World J Immunol 2015; 5(3): 99-112
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2824/full/v5/i3/99.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5411/wji.v5.i3.99