Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Immunol. Jul 27, 2014; 4(2): 107-115
Published online Jul 27, 2014. doi: 10.5411/wji.v4.i2.107
Published online Jul 27, 2014. doi: 10.5411/wji.v4.i2.107
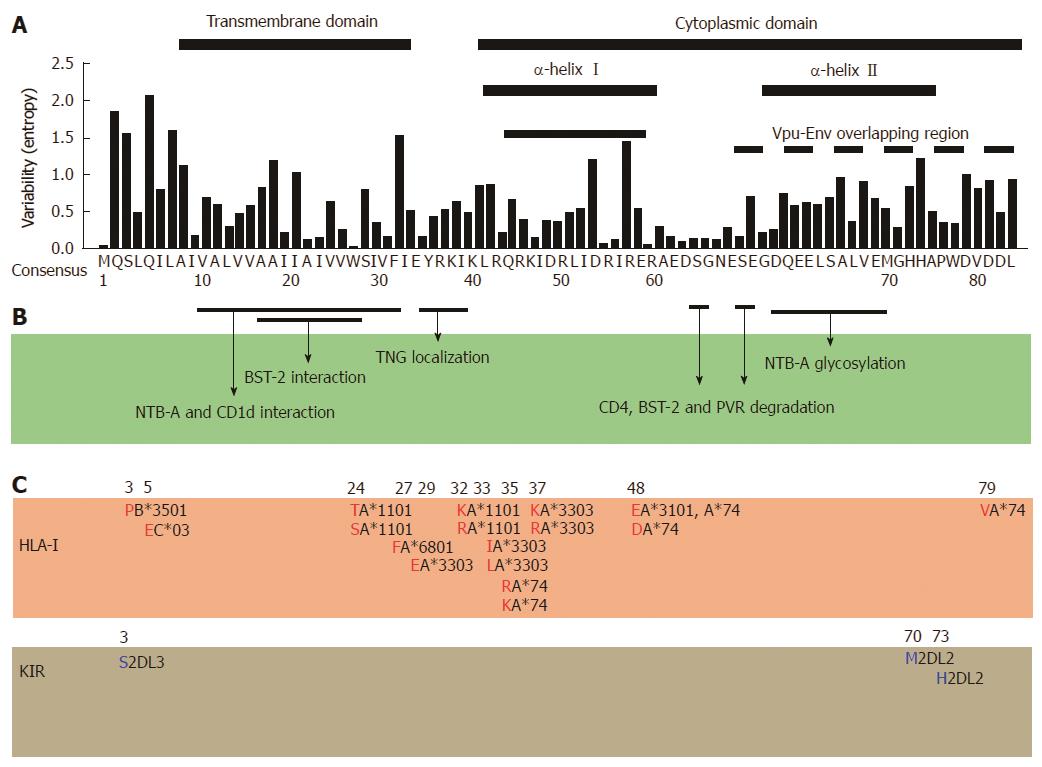
Figure 2 Correlation among amino-acid codon variability, functional regions, and host-mediated immune escape map of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viral protein U.
A: Amino acid codon variability is assigned to each position of Vpu using Shannon entropy approach[24,90]. Sequences were retrieved from Los Alamos database (n =1139), the consensus subtype B sequence is indicated as a reference; B: Interacting positions and domains responsible for the indicated functions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Vpu are shown[14,62,91]; C: Immune escape map shows amino acid codons and residues (red and blue) associated with HLA-I alleles[20,45,50] and killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR)[44], respectively. The specific alleles are indicated in black adjacent to the amino acid.
- Citation: Hasan Z, Kamori D, Ueno T. Role of host immune responses in sequence variability of HIV-1 Vpu. World J Immunol 2014; 4(2): 107-115
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2824/full/v4/i2/107.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5411/wji.v4.i2.107