Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Clin Pediatr. Aug 8, 2016; 5(3): 330-342
Published online Aug 8, 2016. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v5.i3.330
Published online Aug 8, 2016. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v5.i3.330
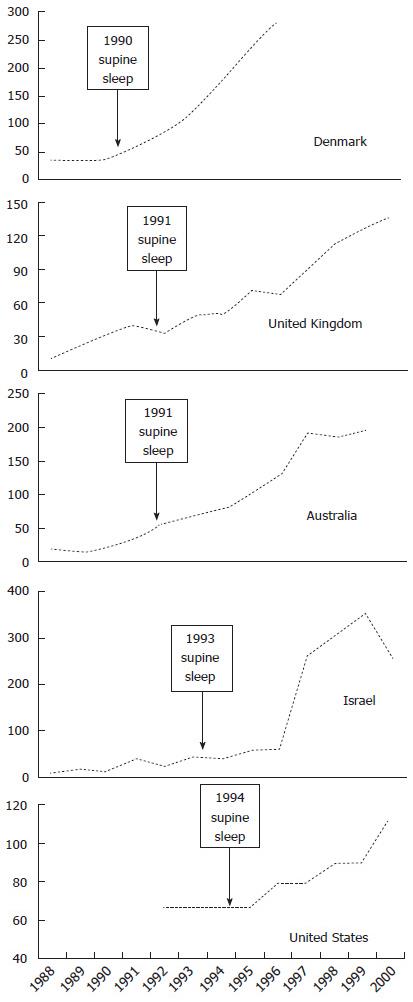
Figure 1 Epidemiological associations with autism rates (dashed line, rate per 10000) and supine sleep campaigns (block arrows).
Autism incidence plotted by reported year of birth cohort, except Israel which is reported from year of insurance claim for infants average 39 mo old (source references in Table 1).
- Citation: Bergman NJ. Hypothesis on supine sleep, sudden infant death syndrome reduction and association with increasing autism incidence. World J Clin Pediatr 2016; 5(3): 330-342
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v5/i3/330.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v5.i3.330