Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Respirol. Nov 28, 2015; 5(3): 188-198
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v5.i3.188
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v5.i3.188
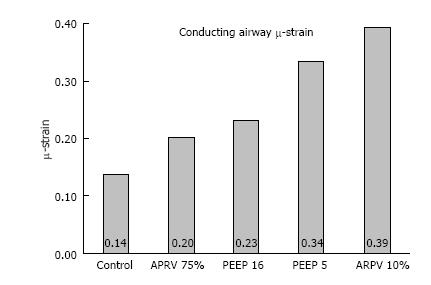
Figure 9 Airway duct μ-strain, was calculated from conducting airway perimeters at inspiration and expiration in all 4 mechanical breath strategies (CMV with PEEP 5 and 10; APRV with TLow at 10% and 75%) tested, plus a Control group with normal lung under mechanical ventilation.
(with permission)[16]. CMV: Conventional mechanical ventilation; APRV: Airway pressure release ventilation.
- Citation: Nieman GF, Gatto LA, Habashi NM. Reducing acute respiratory distress syndrome occurrence using mechanical ventilation. World J Respirol 2015; 5(3): 188-198
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6255/full/v5/i3/188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5320/wjr.v5.i3.188