Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Respirol. Nov 28, 2015; 5(3): 188-198
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v5.i3.188
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v5.i3.188
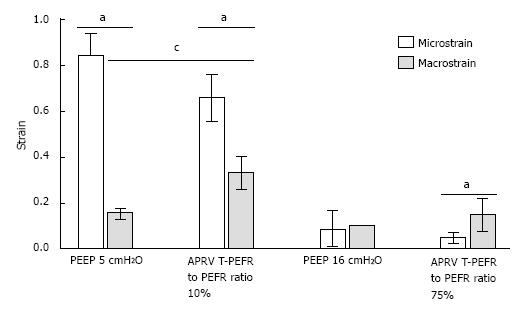
Figure 7 Macro-strain vs micro-strain.
Macro-strain was that calculated for the entire lung and Micro-strain calculated for individual alveoli in the same lung under the identical conditions. Low PEEP (5 cmH2O) with a conventional breath and an extended time at low pressure (10%) with APRV showed the largest difference between Macro- and Micro-strain. High PEEP (16 cmH2O) and a brief time at low pressure with APRV (75%) minimized the differences between Macro- and Micro-strain. See text for description of APRV settings. aP < 0.05 between Macro- and Micro-strain; cP < 0.05 between PEEP 5 and APRV 10 (with permission)[17]. APRV: Airway pressure release ventilation.
- Citation: Nieman GF, Gatto LA, Habashi NM. Reducing acute respiratory distress syndrome occurrence using mechanical ventilation. World J Respirol 2015; 5(3): 188-198
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6255/full/v5/i3/188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5320/wjr.v5.i3.188