Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
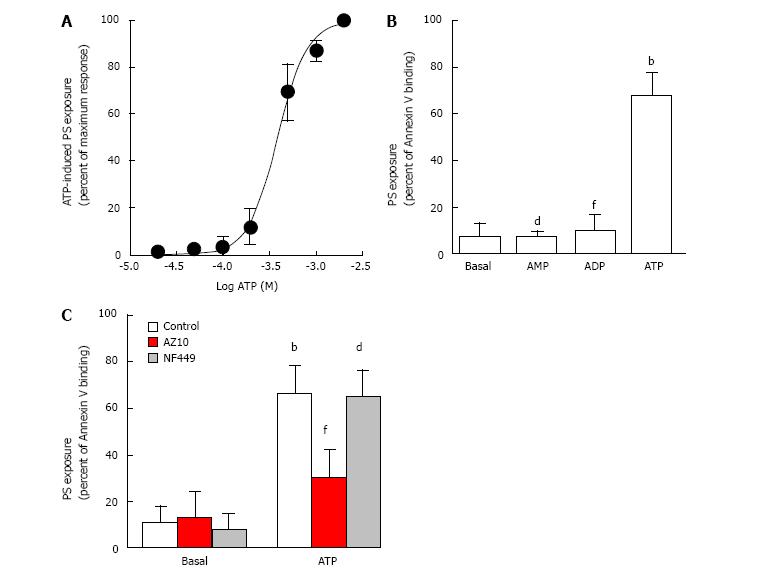
Figure 2 ATP induces phosphatidylserine exposure in canine erythrocytes in a concentration-dependent manner.
Erythrocytes in NaCl medium were incubated for 24 h at 37 °C in the absence or presence of ATP (A) or 1 mmol/L nucleotide (B and C) (as indicated). Prior to ATP incubation, cells were pre-incubated for 15 min in the absence or presence of 10 µmol/L AZ10606120 (AZ10) or 10 µmol/L NF499 (C). Following nucleotide incubation, cells were labeled with FITC-conjugated Annexin V and analyzed by flow cytometry (A-C). A: The data represent percent maximum response to 2 mmol/L ATP (mean ± SD, n = 4 dogs); B: The data represent mean ± SD (n = 5 dogs); bP < 0.001 ATP vs basal; dP < 0.001 AMP vs ATP; fP < 0.001 ADP vs ATP; C: The data represent mean ± SD (n = 5 dogs); bP < 0.001 ATP vs basal; dP < 0.001 ATP with NF449 vs NF449; fP < 0.001 ATP with AZ10606120 vs ATP.
- Citation: Faulks M, Kuit TA, Sophocleous RA, Curtis BL, Curtis SJ, Jurak LM, Sluyter R. P2X7 receptor activation causes phosphatidylserine exposure in canine erythrocytes. World J Hematol 2016; 5(4): 88-93
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6204/full/v5/i4/88.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5315/wjh.v5.i4.88