Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
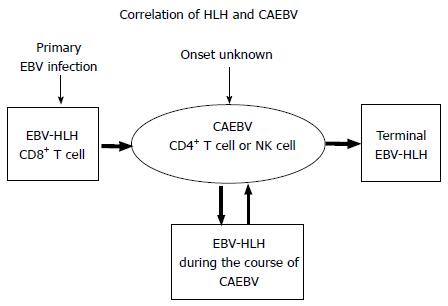
Figure 2 Correlations between hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection status.
CAEBV status may occur without apparent onset of symptoms or may develop following initial acute onset EBV-HLH. During the course of CAEBV, HLH episodes may develop, and if it is not adequately treated by transplantation, most patients eventually succumb to terminal HLH or to lymphoid malignancies. CD8+ T cells play a major role in initial acute onset HLH, whereas CD4+ T cells or NK cells play a role in the status of CAEBV and in CAEBV-related HLH. CAEBV: Chronic active EBV infection; EBV-HLH: Epstein-Barr virus-related hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; NK: Natural killer.
- Citation: Imashuku S. Treatment of Epstein-Barr virus-related hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Study protocol of a prospective pilot study. World J Hematol 2015; 4(4): 69-75
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6204/full/v4/i4/69.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5315/wjh.v4.i4.69