Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Hematol. Nov 6, 2014; 3(4): 118-127
Published online Nov 6, 2014. doi: 10.5315/wjh.v3.i4.118
Published online Nov 6, 2014. doi: 10.5315/wjh.v3.i4.118
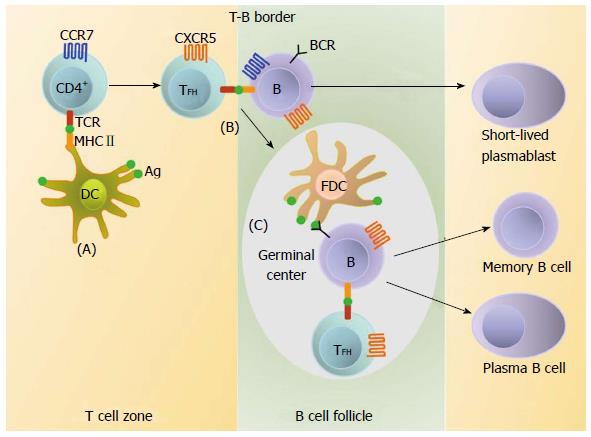
Figure 1 Follicular helper T cells and the differentiation program of B lymphocytes.
A: Naïve CD4+ T cells are activated following recognition of antigen (Ag) presented by dendritic cells (DC) in T cell zones. Upon antigen activation and co-stimulation by DC, nascent TFH upregulate CXC-chemokine receptor 5 (CXCR5), downregulate CC-chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) and migrate towards B cell follicles; B: At the T-B border TFH contact antigen-activated B cells that move to the T-cell zone after upregulating CCR7. TFH deliver help to B cells resulting in their differentiation into short-lived extrafollicular plasmablasts or their migration into B cell-follicles to form germinal centers (GCs); C: Within GC, TFH promotes the B cell differentiation into long-lived plasma cells and memory B cells. TFH: Follicular helper T lymphocytes; FDC: Follicle dendritic cell; BCR: B cell receptor; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; TCR: T cell receptor.
- Citation: Parodi C, Badano MN, Galassi N, Coraglia A, Baré P, Malbrán A, Bracco MME. Follicular helper T lymphocytes in health and disease. World J Hematol 2014; 3(4): 118-127
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6204/full/v3/i4/118.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5315/wjh.v3.i4.118