Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
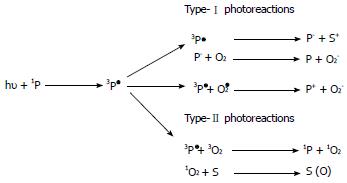
Figure 2 Cellular damage mechanism.
Type-I and Type-II photoreactions, where 1P is a photosensitizer in a singlet ground state, 3P1 is a photosensitizer in a triplet excited state, S is a substrate molecule, Pÿ is reduced photosensitizer molecule, S is an oxidized substrate molecule, O2 is molecular oxygen (triplet ground state), Oÿ2 is the superoxide anion, O2 is the superoxide radical, P is the oxidized photosensitizer, 3O2 is triplet ground-state oxygen, 1O2 is oxygen in a singlet excited state, and S (O) is an oxygen adduct of a substrate (adapted from Macdonald et al[1]).
- Citation: Negosanti L, Pinto V, Sgarzani R, Negosanti F, Zannetti G, Cipriani R. Photodynamic therapy with topical aminolevulinic acid. World J Dermatol 2014; 3(2): 6-14
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6190/full/v3/i2/6.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5314/wjd.v3.i2.6