Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Orthop. Dec 18, 2017; 8(12): 913-921
Published online Dec 18, 2017. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v8.i12.913
Published online Dec 18, 2017. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v8.i12.913
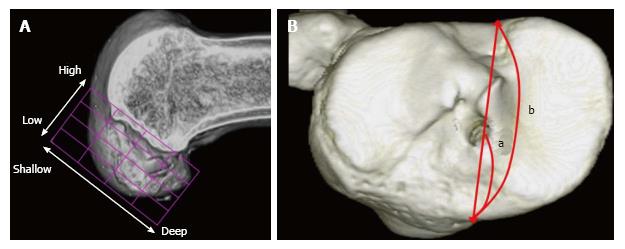
Figure 2 Evaluation of tunnel positions in femur and tibia.
A: 3D CT-based model of a femoral bone tunnel after an ACL reconstruction. Tunnel position was assessed according to the quadrant method[46]. Depth = (distance from the posterior edge to tunnel center along Blumensaat’s line/total length of the lateral condyle) × 100%. Height = (distance from Blumensaat’s line to tunnel center/total height of the intercondylar roof) × 100%; B: For tibial side, Staubli’s technique was used[47]. Anterior-posterior position = (a/b) × 100%. a: Distance from anterior edge to tunnel center; b: Anteroposterior length of the tibia plateau. ACL: Anterior cruciate ligament.
- Citation: Tashiro Y, Okazaki K, Murakami K, Matsubara H, Osaki K, Iwamoto Y, Nakashima Y. Anterolateral rotatory instability in vivo correlates tunnel position after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using bone-patellar tendon-bone graft. World J Orthop 2017; 8(12): 913-921
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v8/i12/913.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v8.i12.913