Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Clin Oncol. Oct 10, 2015; 6(5): 80-88
Published online Oct 10, 2015. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v6.i5.80
Published online Oct 10, 2015. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v6.i5.80
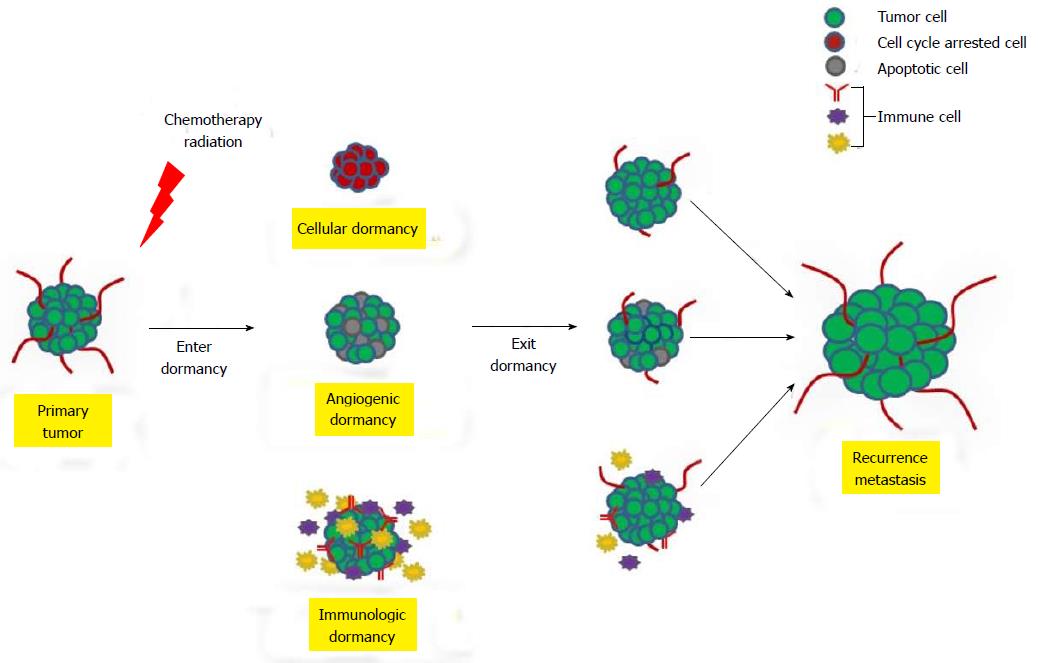
Figure 1 Mechanisms of human tumor dormancy.
Schematic depicting three mechanisms that lead to tumor dormancy after the initial clinical treatment. Tumor dormancy can result from cell cycle arrest (cellular dormancy), tumor size limitation due to a lack of functional blood vessels (angiogenic dormancy), or immunosurveillance (immunologic dormancy). Figure adapted from Almog[16] (2010) and Wang and Lin[6] (2013).
- Citation: Evans EB, Lin SY. New insights into tumor dormancy: Targeting DNA repair pathways. World J Clin Oncol 2015; 6(5): 80-88
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v6/i5/80.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v6.i5.80