Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 10, 2014; 5(5): 874-882
Published online Dec 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.874
Published online Dec 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.874
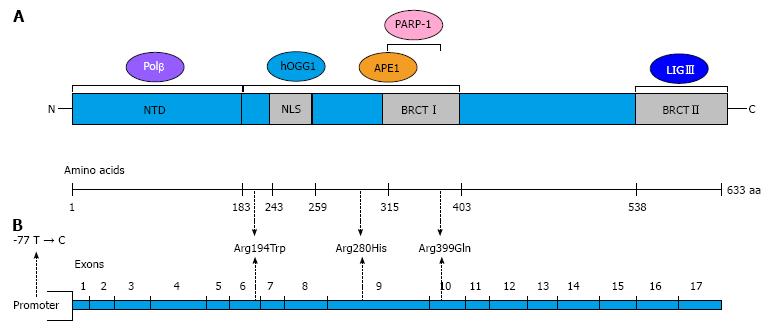
Figure 2 Domains of the X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 protein and X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 gene structure.
A: The schematic diagram shows the regions of interaction with other base excision repair proteins; B: The diagram shows the structure of XRCC1 with the locations of the most common and well-studied single nucleotide polymorphisms: 77 T > C, Arg194Trp, Arg280His and Arg 399Gln. Modified from Sterpone et al[14]. XRCC1: X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1; OGG1: 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1; APE1: Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1; PARP-1: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1; Polβ: DNA polymerase-β; LIGIII: DNA ligase III; NTD: N-terminal domain; NLS: Nuclear localisation signal; BRCT: BRCA1 carbox-terminal domain.
- Citation: Patrono C, Sterpone S, Testa A, Cozzi R. Polymorphisms in base excision repair genes: Breast cancer risk and individual radiosensitivity. World J Clin Oncol 2014; 5(5): 874-882
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v5/i5/874.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.874