Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Aug 15, 2017; 8(3): 117-126
Published online Aug 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i3.117
Published online Aug 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i3.117
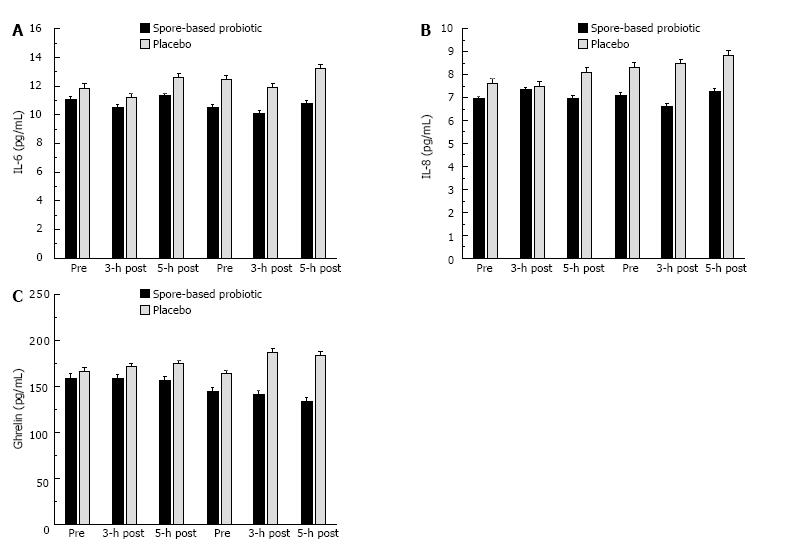
Figure 5 Serum IL-6 (A), IL-8 (B), and MCP-1 (C) response to consumption of a commercially available high-fat, high-calorie pizza meal.
Venous blood samples were collected following an overnight fast and abstention from exercise. Serum samples were analyzed using an automated chemistry analyzer. Subjects consumed an oral probiotic supplement for 30-d and the experimental meal challenge was completed at baseline and following the 30-d supplementation period. Probiotic responses were compare to placebo. While effects did not reach statistical significance, trends are consistent with other variables that did significant change (Figures 2 and 3). IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: McFarlin BK, Henning AL, Bowman EM, Gary MA, Carbajal KM. Oral spore-based probiotic supplementation was associated with reduced incidence of post-prandial dietary endotoxin, triglycerides, and disease risk biomarkers. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2017; 8(3): 117-126
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v8/i3/117.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v8.i3.117