Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2015; 7(12): 438-447
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.438
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.438
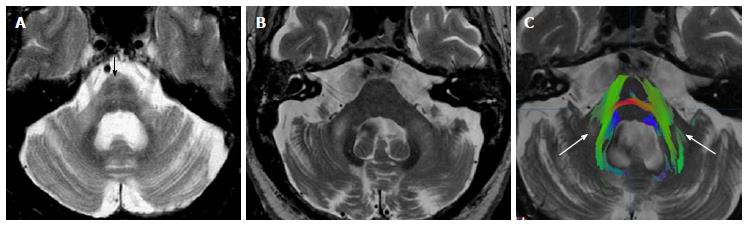
Figure 11 Multiple system atrophy C type and fragile-X associated tremor-ataxia syndrome.
Axial T2 (A) in a patient with MSA-C show typical atrophy of the pons and MCP with degeneration of the pontine crossing fibers (“hot cross bun” sign, black arrow). There is also associated increased T2 signal of the MCP bilaterally. Axial T2 (B) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) tractography (C) in a patient with FXTAS show cerebellar volume loss and associated increased T2 signal and volume loss of MCP. Due to decreased fractional anisotropy (white arrows on C) there is lack of fibers in the areas of abnormal T2 signal. (DTI acquisition technique similar than Figure 1, please see figure for details). Image (B) courtesy of Dr. Andrew Duker. FXTAS: Fragile-X associated tremor-ataxia syndrome; MSA-C: Multiple system atrophy C type; MCP: Middle cerebellar peduncles.
- Citation: Morales H, Tomsick T. Middle cerebellar peduncles: Magnetic resonance imaging and pathophysiologic correlate. World J Radiol 2015; 7(12): 438-447
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v7/i12/438.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.438