Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Radiol. Oct 28, 2021; 13(10): 327-343
Published online Oct 28, 2021. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v13.i10.327
Published online Oct 28, 2021. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v13.i10.327
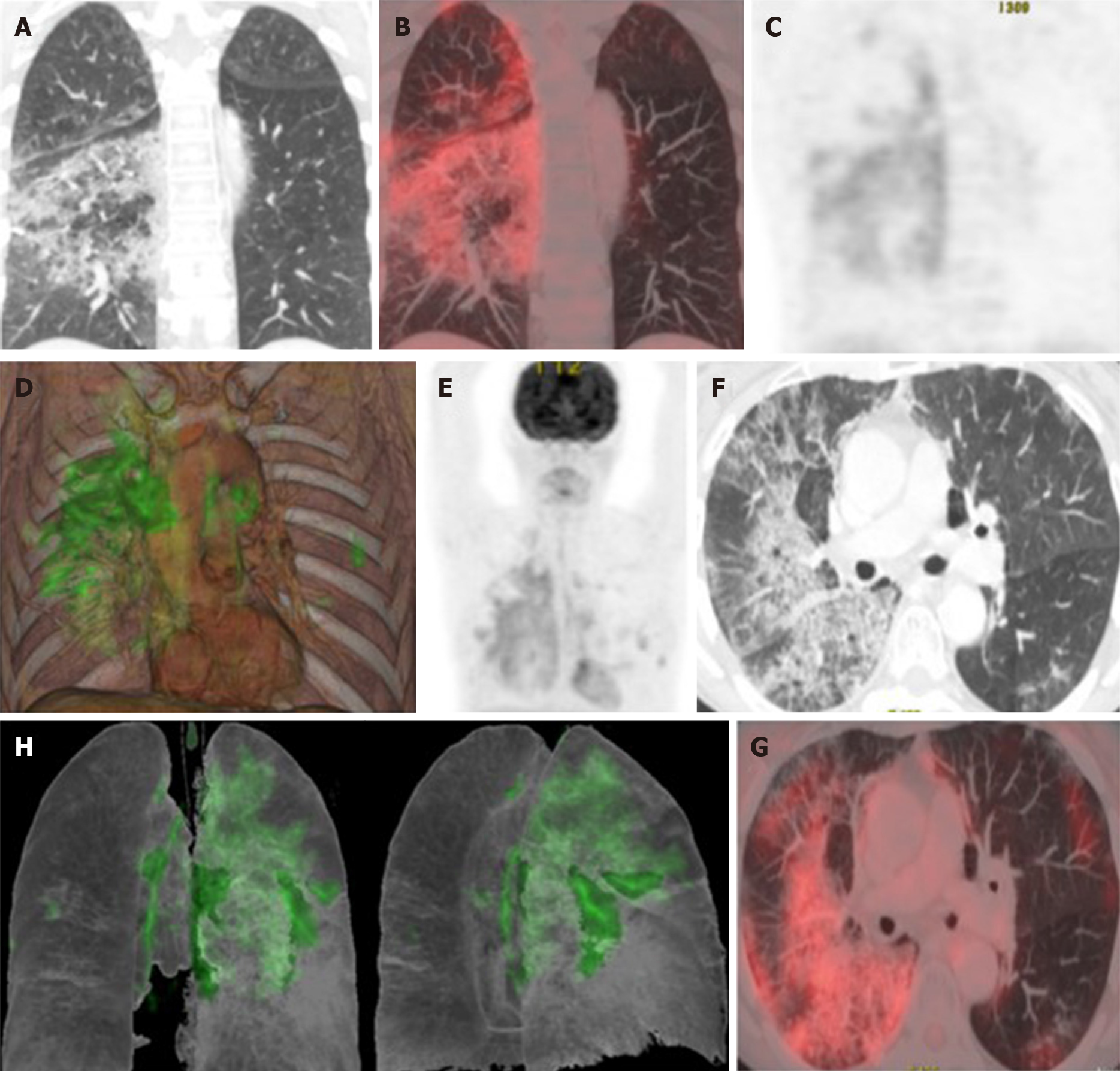
Figure 10 Taken from Landete et al[12], A 65-year-old patient with a history of invasive lepidic-predominant adenocarcinoma (stage pT1bNxM0) treated with surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
A: Coronal computed tomography (CT) showing the crazy paving pattern with a markedly asymmetric bilateral distribution, mainly affecting the right side. B: Positron emission tomography-CT (PET-CT) coronal section. C: Metabolic PET. D: Volume rendering 3D PET-CT. E: MIP, PET. Images B–E reveal an increased cellular activity [standard uptake value (SUV) 4-6] related to the associated inflammatory process and a PET-CT pattern of bilateral coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) with viral pneumonitis, predominantly right-sided. F: Axial CT showing crazy paving pattern with a bilateral, yet markedly asymmetric distribution, predominant right-sided. G and H: Axial section and 3D volume rendering from PET-CT metabolic imaging revealing increased cellular activity (SUV 4-6) related to the associated inflammatory process. PET-CT pattern of bilateral, predominantly right-sided, COVID-19 viral pneumonitis. Citation: Landete P, Quezada Loaiza CA, Aldave-Orzaiz B, Muñiz SH, Maldonado A, Zamora E, Sam Cerna AC, Del Cerro E, Alonso RC, Couñago F. Clinical features and radiological manifestations of COVID-19 disease. World J Radiol 2020; 12(11): 247-260. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc[12]”.
- Citation: Churruca M, Martínez-Besteiro E, Couñago F, Landete P. COVID-19 pneumonia: A review of typical radiological characteristics. World J Radiol 2021; 13(10): 327-343
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v13/i10/327.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v13.i10.327