Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Cardiol. Jul 26, 2014; 6(7): 531-538
Published online Jul 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i7.531
Published online Jul 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i7.531
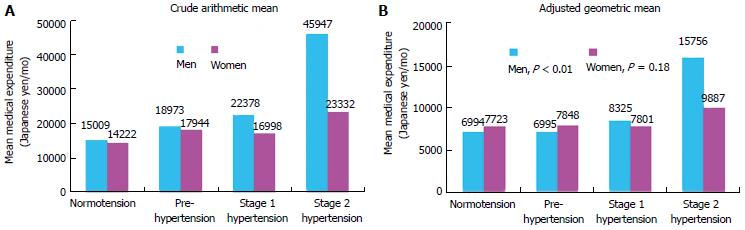
Figure 1 Crude arithmetic mean (A) and adjusted geometric mean (B) of medical expenditure per month over 10 years of follow-up in male and female Japanese medical insurance beneficiaries aged 40-69 years, grouped according to sex and hypertension status.
Analysis of covariance was used to compare log-transformed monthly medical expenditure in each blood pressure category, after adjustment for age, body mass index, smoking habit, drinking habit, serum total cholesterol, and a history of diabetes. From Nakamura et al[6].
- Citation: Nakamura K, Okamura T, Miura K, Okayama A. Hypertension and medical expenditure in the Japanese population: Review of prospective studies. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(7): 531-538
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i7/531.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i7.531