Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Cardiol. Sep 26, 2023; 15(9): 415-426
Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v15.i9.415
Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v15.i9.415
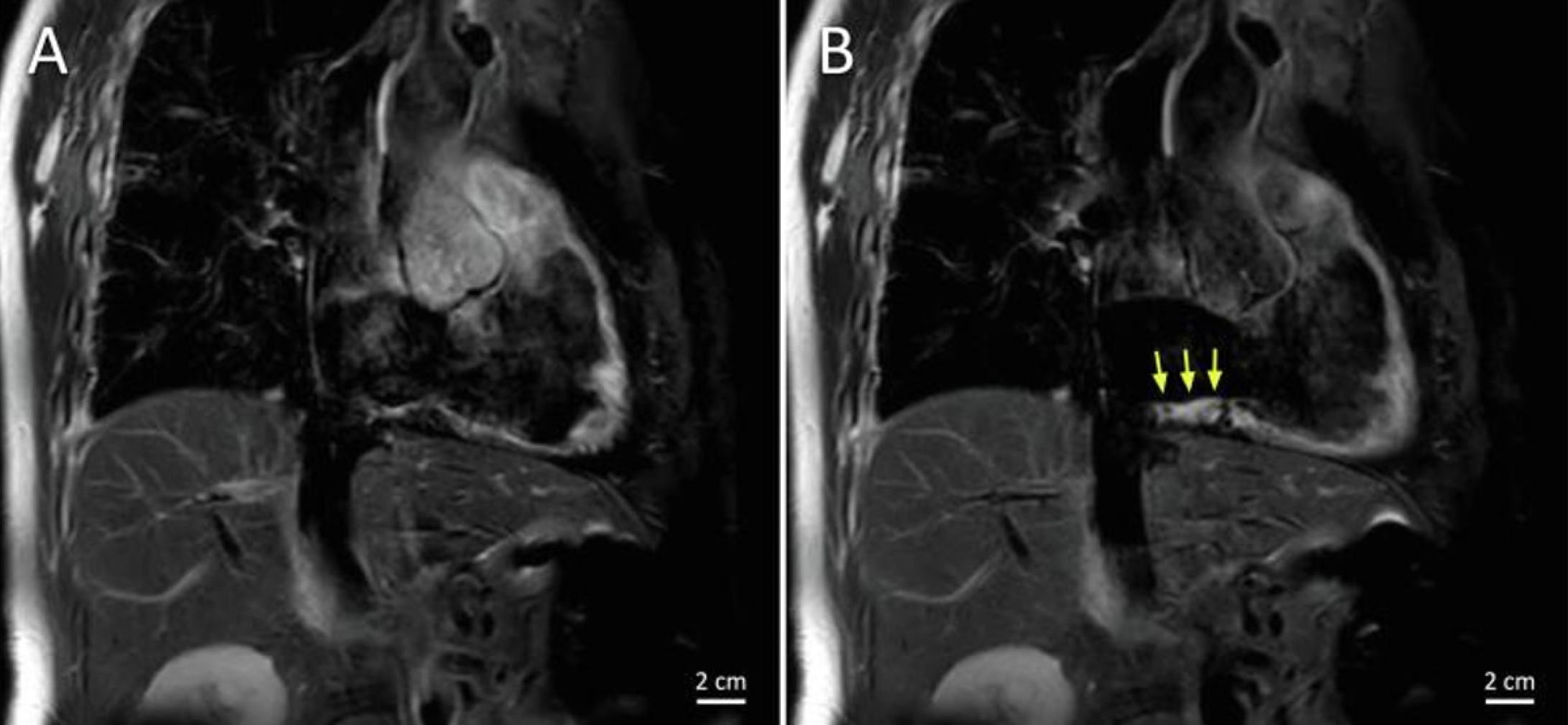
Figure 4 Imaging with T2 mapping detects inflamed edematous tissue.
A and B: T2-weighted magnetic resonance images of the cavotricuspid isthmus in the RAO view before (A) and after (B) ablation showing edema in the ablation lesions, indicated by the yellow arrows. Citation: Bijvoet GP, Holtackers RJ, Nies HMJM, Mihl C, Chaldoupi SM. The role of interventional cardiac magnetic resonance (iCMR) in a typical atrial flutter ablation: The shortest path may not always be the fastest. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc 2022; 41: 101078. [PMID: 35800043 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2022.101078]. Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. (Reproduced under the terms of the Creative Commons CC-BY license)[44].
- Citation: Tampakis K, Pastromas S, Sykiotis A, Kampanarou S, Kourgiannidis G, Pyrpiri C, Bousoula M, Rozakis D, Andrikopoulos G. Real-time cardiovascular magnetic resonance-guided radiofrequency ablation: A comprehensive review. World J Cardiol 2023; 15(9): 415-426
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v15/i9/415.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v15.i9.415