Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Cardiol. Apr 26, 2022; 14(4): 220-230
Published online Apr 26, 2022. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v14.i4.220
Published online Apr 26, 2022. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v14.i4.220
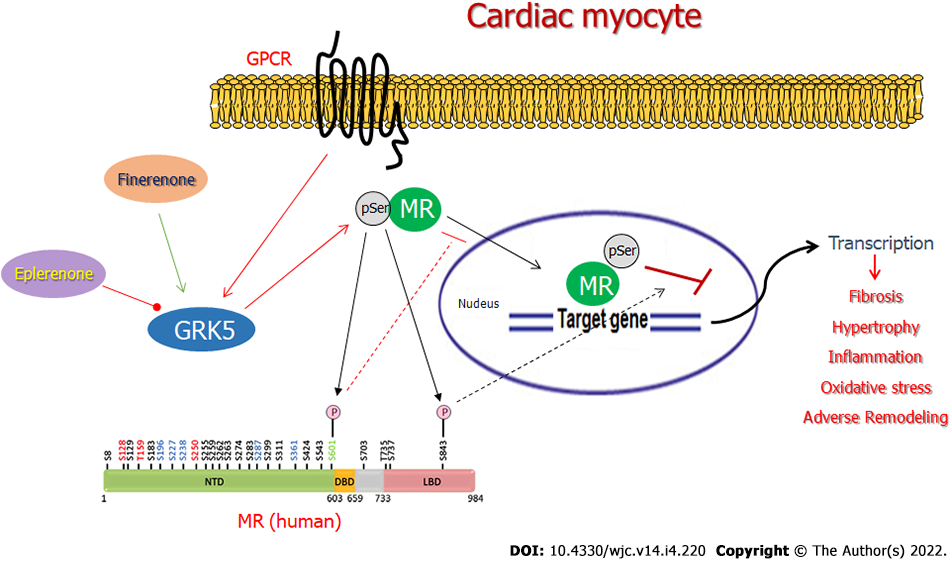
Figure 5 Schematic illustration of the differential effects of finerenone vs eplerenone on G protein-coupled receptor-kinase 5-dependent repression of the cardiac mineralocorticoid receptor.
Finerenone, unlike eplerenone, stimulates G protein-coupled receptor-kinase (GRK)-5 to phosphorylate the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR). The two main (putative) GRK5 phosphorylation sites on the human MR protein, Ser601 and Ser843, are highlighted, along with their functional impacts for the MR (pSer601 blocks nuclear translocation; pSer843 suppresses Aldo-induced transcriptional activity)[24,30]. GPCR: G protein-coupled receptor; NTD: N-terminal domain; DBD: DNA-binding domain; LBD: Ligand-binding domain; pSer: Phosphoserine. See text for more details and for all other molecular acronyms' descriptions.
- Citation: Pollard CM, Suster MS, Cora N, Carbone AM, Lymperopoulos A. GRK5 is an essential co-repressor of the cardiac mineralocorticoid receptor and is selectively induced by finerenone. World J Cardiol 2022; 14(4): 220-230
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v14/i4/220.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v14.i4.220