Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Cardiol. Mar 26, 2022; 14(3): 139-151
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v14.i3.139
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v14.i3.139
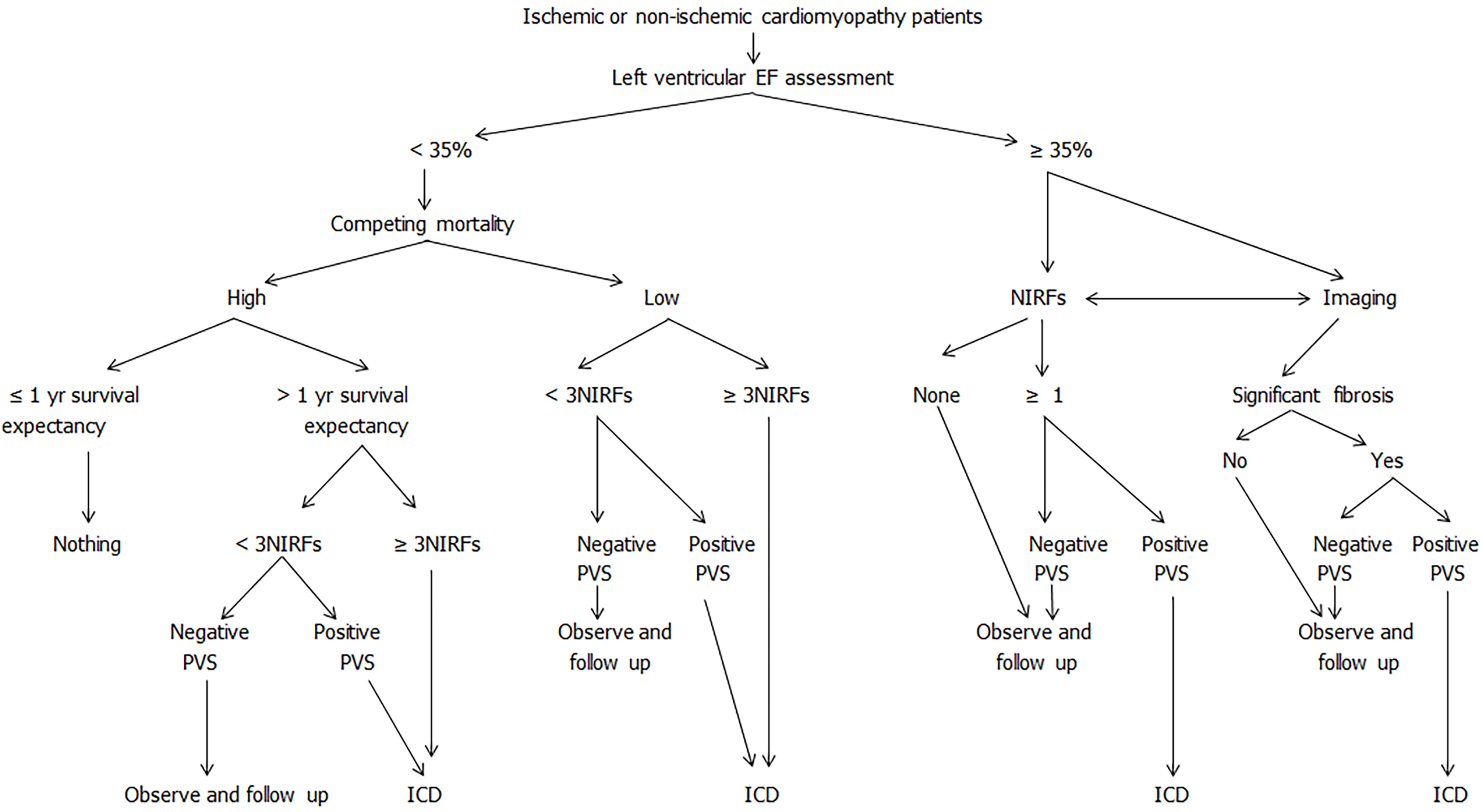
Figure 2 Emerging new sudden cardiac death risk stratification paradigm.
It is based on newer evidence, incorporating competing mortality assessments, as well as non-invasive and invasive tests. Non-invasive tests are performed before programmed ventricular stimulation (PVS) to assess the likelihood of functional circuit formation. PVS is pivotal in determining the potential for arrhythmia sustainability and guiding treatment, especially in intermediate and low‐risk patients. “Observe and Follow‐up” involves repeating tests for NIRF annually and PVS every 3–5 yr. NIRFs (noninvasive ECG risk factors) including the presence of late potentials (≥ 2/3 criteria), frequent premature ventricular contractions (≥ 30/h), non-sustained VT (≥ 1/24 h), abnormal heart rate turbulence (onset ≥ 0% and slope ≤ 2.5ms) and reduced deceleration capacity (≤ 4.5 ms), positive T wave alternans (≥ 65 μV), decreased heart rate variability (SDNN < 70ms), prolonged QTc interval (> 440 ms in males and > 450 ms in females). (Modified after permission from ANE[60]).
- Citation: Arsenos P, Gatzoulis KA, Tsiachris D, Dilaveris P, Sideris S, Sotiropoulos I, Archontakis S, Antoniou CK, Kordalis A, Skiadas I, Toutouzas K, Vlachopoulos C, Tousoulis D, Tsioufis K. Arrhythmic risk stratification in ischemic, non-ischemic and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: A two-step multifactorial, electrophysiology study inclusive approach. World J Cardiol 2022; 14(3): 139-151
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v14/i3/139.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v14.i3.139