Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Cardiol. Jul 26, 2020; 12(7): 303-333
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v12.i7.303
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v12.i7.303
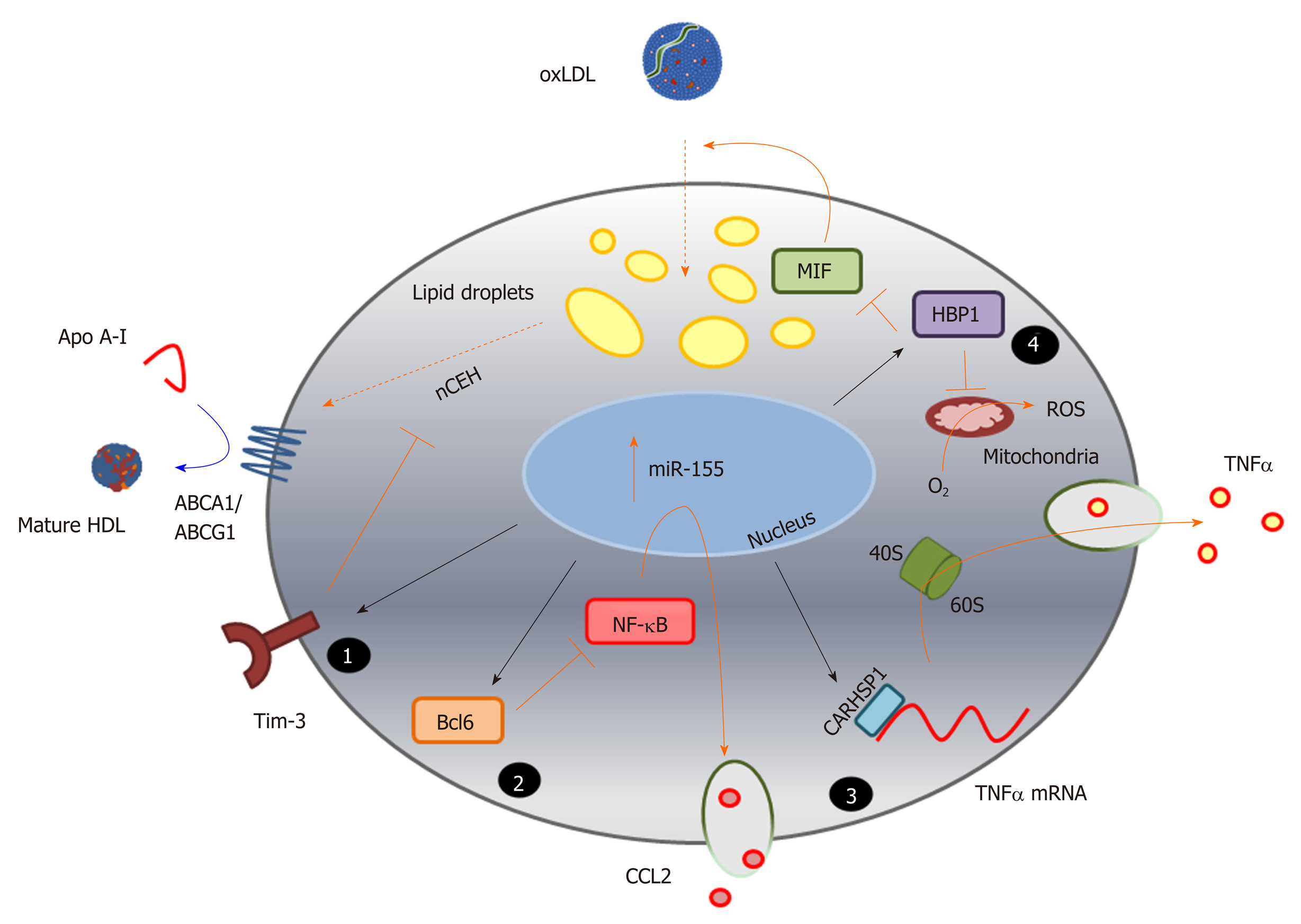
Figure 3 Identification of novel pathways associated with foam cell formation.
MicroRNA sequences altered during macrophage foam cell formation reveal novel pathways involved in this process, and highlight the complexity of miRNA function in targeting multiple gene pathways, exemplified here by miR-155 (Table 1). Inhibition of expression of the cell surface immunoregulatory glycoprotein, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3 (Tim-3), by miR-155 (1) increases hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters by neutral cholesteryl ester hydrolase, and promotes efflux of this lipid via ATP binding cassette transporter A1 and ATP binding cassette transporter G1, to apolipoprotein A-I and high density lipoprotein respectively. MicroRNA-155 also represses expression of the transcriptional repressor B-cell lymphoma 6 protein[236], which increases nuclear factor kappa beta activity and enhances production of the chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 (2); Repression of the cytoplasmic protein, calcium-regulated heat stable protein (CARHSP1) by miR-155, results in reduced binding of this protein to the 3’UTR of the TNFα gene transcript, and to reduced mRNA stability and decreased output of this cytokine (3); MicroRNA-155 also directly targets (represses) HMG-Box transcription factor 1, thereby increasing production of reactive oxygen species and loss of inhibition of macrophage migration inhibitory factor, leading to increased oxidatively modify proteoglycan-bound low density lipoprotein uptake and lipid accumulation (4). The black arrows represent direct targeting by miR-155; orange bars and arrows represent the functions of miR-155 targets in the absence of this miRNA sequence. HDL: High density lipoprotein; ABCA1: ATP binding cassette transporter A1; ABCG1: ATP binding cassette transporter G1; ACAT-1: Acyl-CoA cholesteryl acyl transferase or sterol O-acyltransferase 1; ApoA-I: Apolipoprotein A-I; Bcl6: B-cell lymphoma 6 protein; CARHSP1: Calcium-regulated heat stable protein; CCL2: C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; HBP1: HMG-Box transcription factor 1; MIF: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa beta; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor alpha.
- Citation: Lightbody RJ, Taylor JMW, Dempsie Y, Graham A. MicroRNA sequences modulating inflammation and lipid accumulation in macrophage “foam” cells: Implications for atherosclerosis. World J Cardiol 2020; 12(7): 303-333
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v12/i7/303.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v12.i7.303