Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Biol Chem. Feb 26, 2016; 7(1): 110-127
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.110
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.110
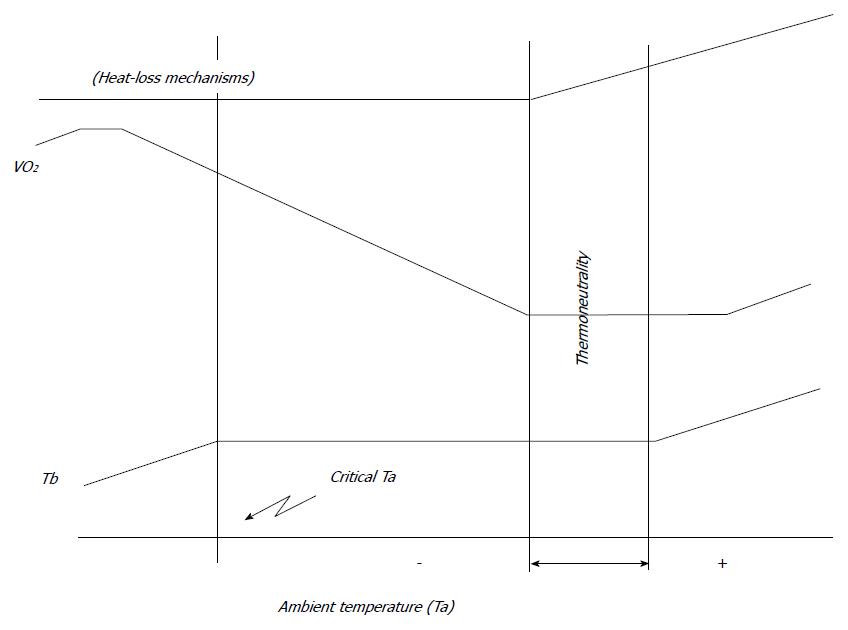
Figure 4 Relation among O2 consumption increases in ambient temperature and thermoregulation in animals.
When ambient Ta decreases below thermoneutrality, VO2 increases maintaining body Tb. When thermogenesis does not suffice, Tb begins to fall (critical Ta). The ability to maintain a thermoneutral range is mostly due to an increase in heat dissipation. Eventually, with further increases in Ta, heat-loss mechanisms will not prevent a rise in Tb, which will also lead to a rise in VO2[162]. Ta: Temperature; VO2: Oxygen consumption; Tb: Temperature.
- Citation: Paital B, Panda SK, Hati AK, Mohanty B, Mohapatra MK, Kanungo S, Chainy GBN. Longevity of animals under reactive oxygen species stress and disease susceptibility due to global warming. World J Biol Chem 2016; 7(1): 110-127
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v7/i1/110.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.110