Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Biol Chem. Aug 26, 2015; 6(3): 83-94
Published online Aug 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.83
Published online Aug 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.83
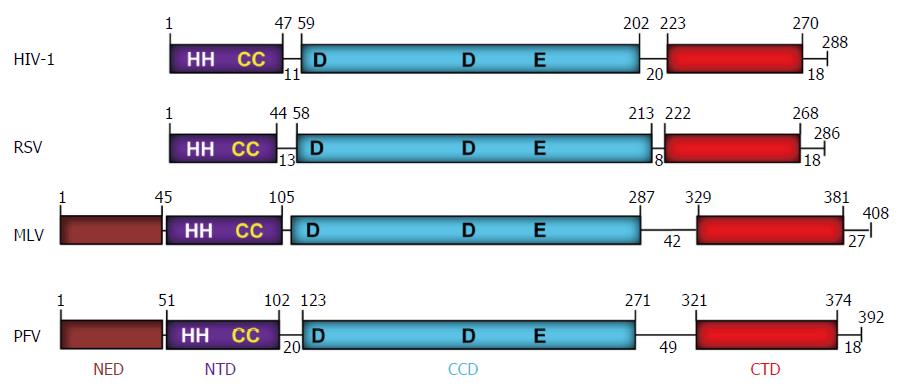
Figure 2 Domain organization of retroviral integrases.
The domains (NED: N-terminal extension domain; NTD: N-terminal domain; CCD: Catalytic core domain; and CTD: C-terminal domain) are depicted with different colors. The number of residues in each domain are indicated. The domains are separated by protein linkers of various sizes. NTD contains the zinc binding HH-CC motif and the D-D-35-E motif in CCD binds Mg2+ which constitutes the active site. The CTD shows a topology of SH3-like domain, a characteristic feature associated with protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions. The exact MLV domain sizes have not been determined experimentally except for the CTD[99]. A short tail of disordered amino acids is located on the C-terminal end of each IN. IN: Integrase; HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus; RSV: Rous sarcoma virus; MLV: Murine leukemia; PFV: Prototype foamy virus.
- Citation: Grandgenett DP, Pandey KK, Bera S, Aihara H. Multifunctional facets of retrovirus integrase. World J Biol Chem 2015; 6(3): 83-94
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v6/i3/83.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.83