Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 26, 2014; 5(4): 409-428
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i4.409
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i4.409
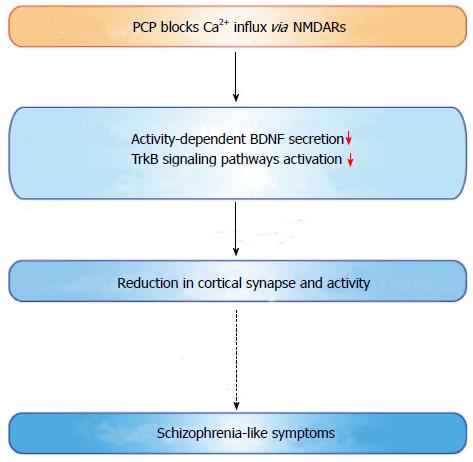
Figure 3 Molecular mechanisms of phencyclidine-induced synaptic loss as a cellular model of schizophrenia.
Phencyclidine decreased the number of synaptic sites in cultured cortical neurons through blockade of Ca2+ influx via NMDARs and resultant suppression of BDNF secretion. The impairment in BDNF secretion reduced TrkB activation and resulted in decreased synaptic connectivity[15]. BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; NMDAR: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors; PCP: Phencyclidine.
- Citation: Adachi N, Numakawa T, Richards M, Nakajima S, Kunugi H. New insight in expression, transport, and secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor: Implications in brain-related diseases. World J Biol Chem 2014; 5(4): 409-428
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i4/409.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i4.409