Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2014; 5(2): 180-203
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.180
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.180
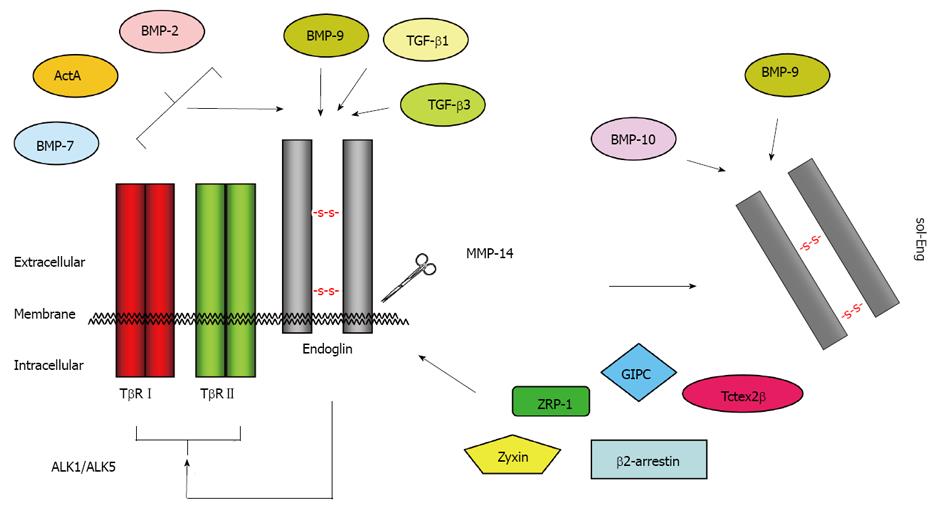
Figure 4 Binding partners of endoglin.
Endoglin physically interacts via its extracellular domain with TGF-β1, TGF-β3 and BMP-9[110]. The short cytoplasmic domain has affinity for ZRP-1[63], Zyxin[64], GIPC[67], β-arrestin-2[66], and Tctex2β[65]. In conjunction with TβRI and TβRII, the binding spectrum is extended to BMP-2, BMP-7 and ActA[111]. After proteolytic cleavage (shedding) by MMP-14 (also known as membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase MT1-MMP), the soluble form of endoglin (sol-Eng) is released[59]. This form has capacity to bind BMP-9 and BMP-10[113]. TGF: Transforming growth factor; BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein.
- Citation: Meurer SK, Alsamman M, Scholten D, Weiskirchen R. Endoglin in liver fibrogenesis: Bridging basic science and clinical practice. World J Biol Chem 2014; 5(2): 180-203
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i2/180.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.180