Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Jan 26, 2012; 3(1): 7-26
Published online Jan 26, 2012. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v3.i1.7
Published online Jan 26, 2012. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v3.i1.7
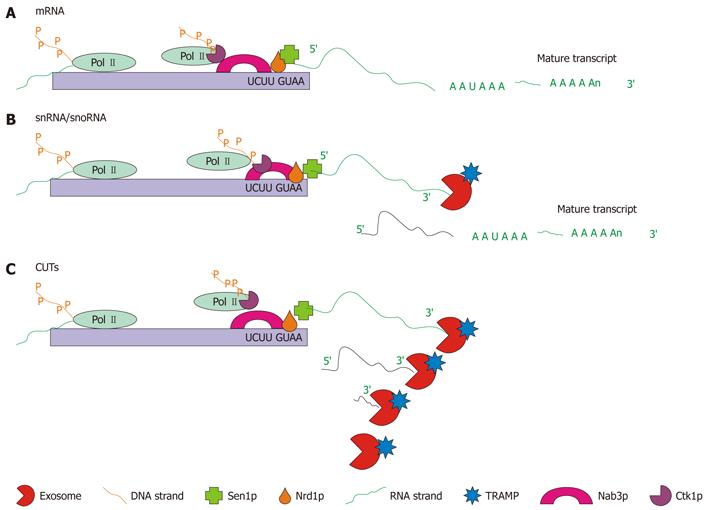
Figure 7 Schematic representation of the three types of Nrd1p/Nab3p-dependent RNA maturation.
A: mRNA 3′ end trimming: for some mRNAs, the Nrd1p complex is required to complete transcription. Pictured is the Nrd1p complex associated with Pol II bound to the Nrd1p and Nab3p binding sites, which cause the Pol II molecule to lift off of the DNA and release the RNA. At this point a poly(A) polymerase (not shown) polyadenylates the end of the strand producing the mature mRNA; B: snRNA/snoRNA 3′ end trimming: snRNA and snoRNA, which are transcribed from autonomous transcription units, are terminated by the Nrd1p complex. Pictured is the Nrd1p complex which causes transcription termination. Following polyadenylation by the TRAMP complex and 3′ end trimming by the exosome, the mature transcript is formed; C: Cryptic unstable transcript (CUT) degradation: transcription of CUTs is also terminated by the Nrd1p complex. Pictured is the Nrd1p complex interacting with Pol II causing transcription termination. Following termination the transcript is degraded by the exosome in conjunction with the TRAMP complex[86,95].
- Citation: Bernstein J, Toth EA. Yeast nuclear RNA processing. World J Biol Chem 2012; 3(1): 7-26
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v3/i1/7.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v3.i1.7