Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Jan 26, 2012; 3(1): 7-26
Published online Jan 26, 2012. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v3.i1.7
Published online Jan 26, 2012. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v3.i1.7
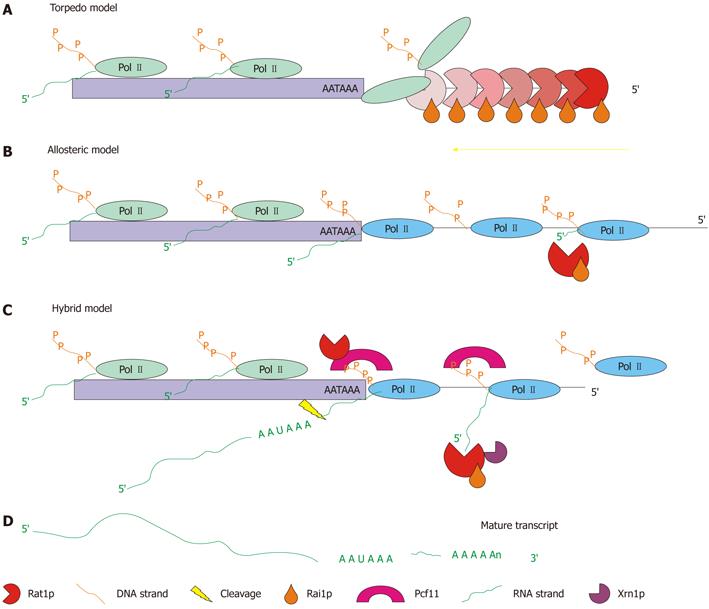
Figure 2 Schematic representation of the three possible modes of operation for the 5′→3′ exonuclease pathway.
A: Torpedo model-the Rat1p/Rai1p complex acts as a wedge to torpedo the polymerase from the DNA strand and terminate transcription[53,54]; B: Allosteric model-the positioning element for the poly(A) site (AATAAA) causes a change in the conformation of the polymerase causing a gradual stop in transcription. The Rat1p/Rai1p complex is used to eliminate RNA downstream of the poly(A) site[55]; C: Hybrid model-the positioning element for the poly(A) site causes a change in the conformation of the polymerase, while Rat1p and Pcf11 also cause a pause in transcription. Termination is gradual but faster than that in the allosteric model. Rat1p/Rai1p are still utilized to remove RNA transcribed downstream of the poly(A) site (adapted from[56]); D: The end result of each model is a mature transcript.
- Citation: Bernstein J, Toth EA. Yeast nuclear RNA processing. World J Biol Chem 2012; 3(1): 7-26
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v3/i1/7.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v3.i1.7