Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 21, 2019; 10(3): 44-64
Published online Nov 21, 2019. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v10.i3.44
Published online Nov 21, 2019. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v10.i3.44
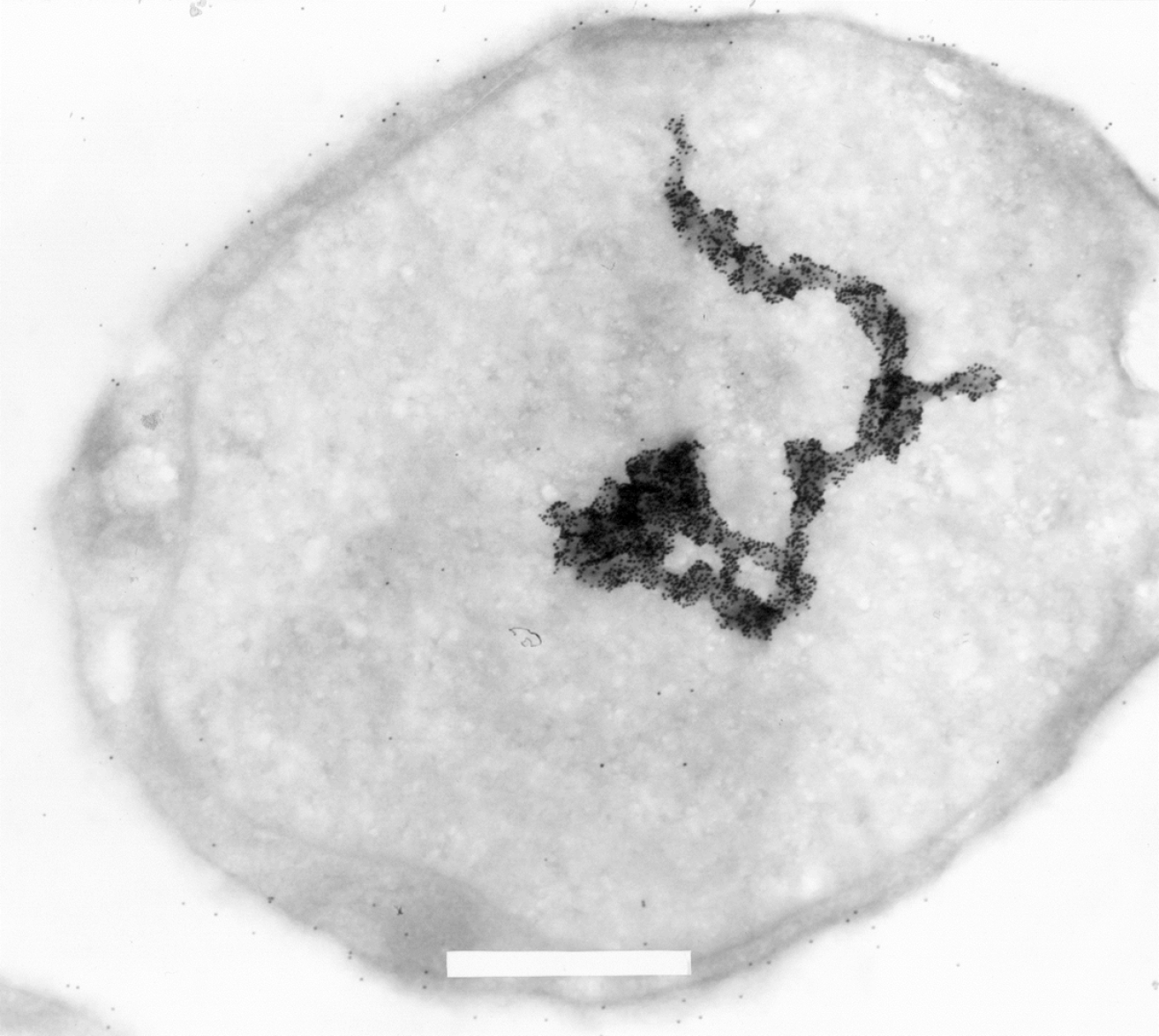
Figure 5 Electron microscopic image of a L540 Hodgkin-derived cell labeled with 15 nm gold-particle-coupled Ki-1 antibody (× 29.
000 fold magnification). Some labeling on the cell surface is due to Ki-1 binding to the CD30 cell surface receptor. Strong hyaluronic acid binding protein 4 (HABP4) labeling can be detected in the nucleus and the format of the large macrostructure seems to represent part of a chromosome or also (transcriptionally active?) chromatin. A part of the upper end of the macrostructure seems to follow a “corkscrew”-like pattern. Each small black dot is a single Ki-1 gold labeled antibody. Please see[3] for more experimental details. In brief, cells were pelleted by centrifugation. The cell pellet was solidified on ice and the solid cell block was prepared in slices of 2 mm that were dehydrated by incubation in a solution containing stepwise increasing sucrose concentration up to 70%. After fixation in frozen nitrogen, ultrathin cryosections were prepared with an ultracut E, FC-4D and collected on nickel grids. After incubation with Ki-1 antibody, washing, and incubation with secondary reagent Staphylococcal aureus protein A-gold labeled, and further washing, the sections were fixed and contrasted with 4% uranyl acetate to be subsequently analyzed in a Siemens Elmiskop 101, Electron Microscope. We would like to thank Prof. Dr. Hilmar Lemke (Kiel, Germany) for generously providing the electron micrography.
- Citation: Colleti C, Melo-Hanchuk TD, da Silva FRM, Saito Â, Kobarg J. Complex interactomes and post-translational modifications of the regulatory proteins HABP4 and SERBP1 suggest pleiotropic cellular functions. World J Biol Chem 2019; 10(3): 44-64
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v10/i3/44.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v10.i3.44