Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Aug 26, 2010; 1(8): 239-247
Published online Aug 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i8.239
Published online Aug 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i8.239
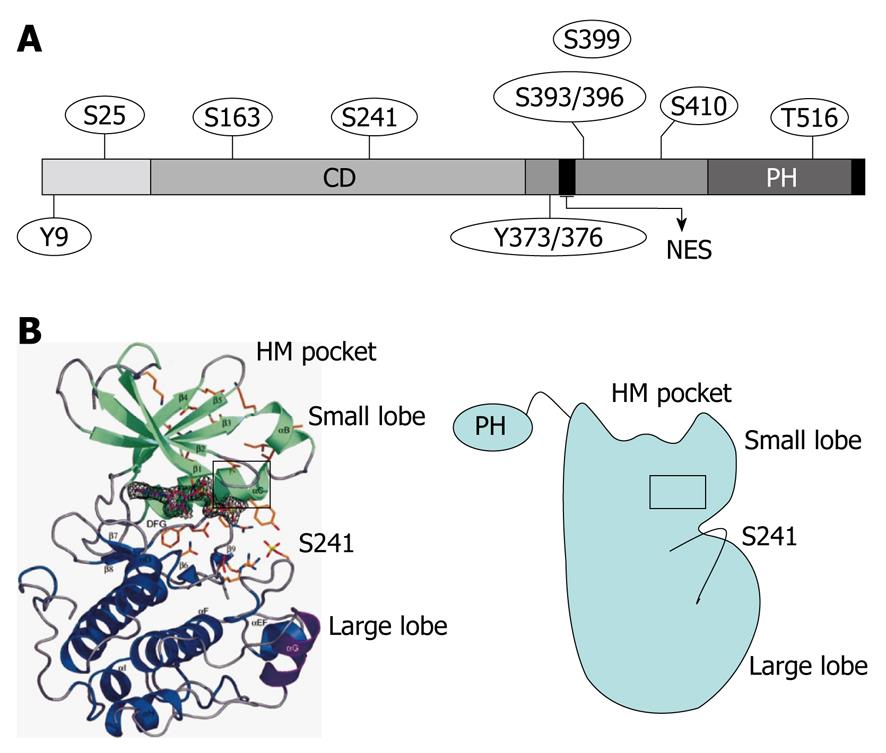
Figure 1 Secondary structure and phosphorylation sites of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1.
A: 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) consists of an N-terminal kinase catalytic domain (CD; amino acids 71-359) and a C-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain (amino acids 459-550). The nuclear export sequence (NES) (amino acids 379-388) is essential for exporting PDK1 into the cytoplasm from the nucleus. The phosphorylation sites of PDK1 include Ser-241 and Tyr-373/376, which is dependent on Tyr-9 and required for PDK1 catalytic activity; B: Crystal structure of the human PDK1 kinase domain. Residues 71-163 are green (small lobe) and residues 164-358 are blue (large lobe). The αC-helix (amino acids 124-136) is boxed in black and encompasses residues 287-295, which are purple. The hydrophobic motif (HM) pocket with the Ser-241 in the activation loop is also shown. This figure was adopted from Biondi et al[26], 2002.
- Citation: Li Y, Yang KJ, Park J. Multiple implications of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 in human cancer. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(8): 239-247
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i8/239.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i8.239