Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2010; 1(5): 95-102
Published online May 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.95
Published online May 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.95
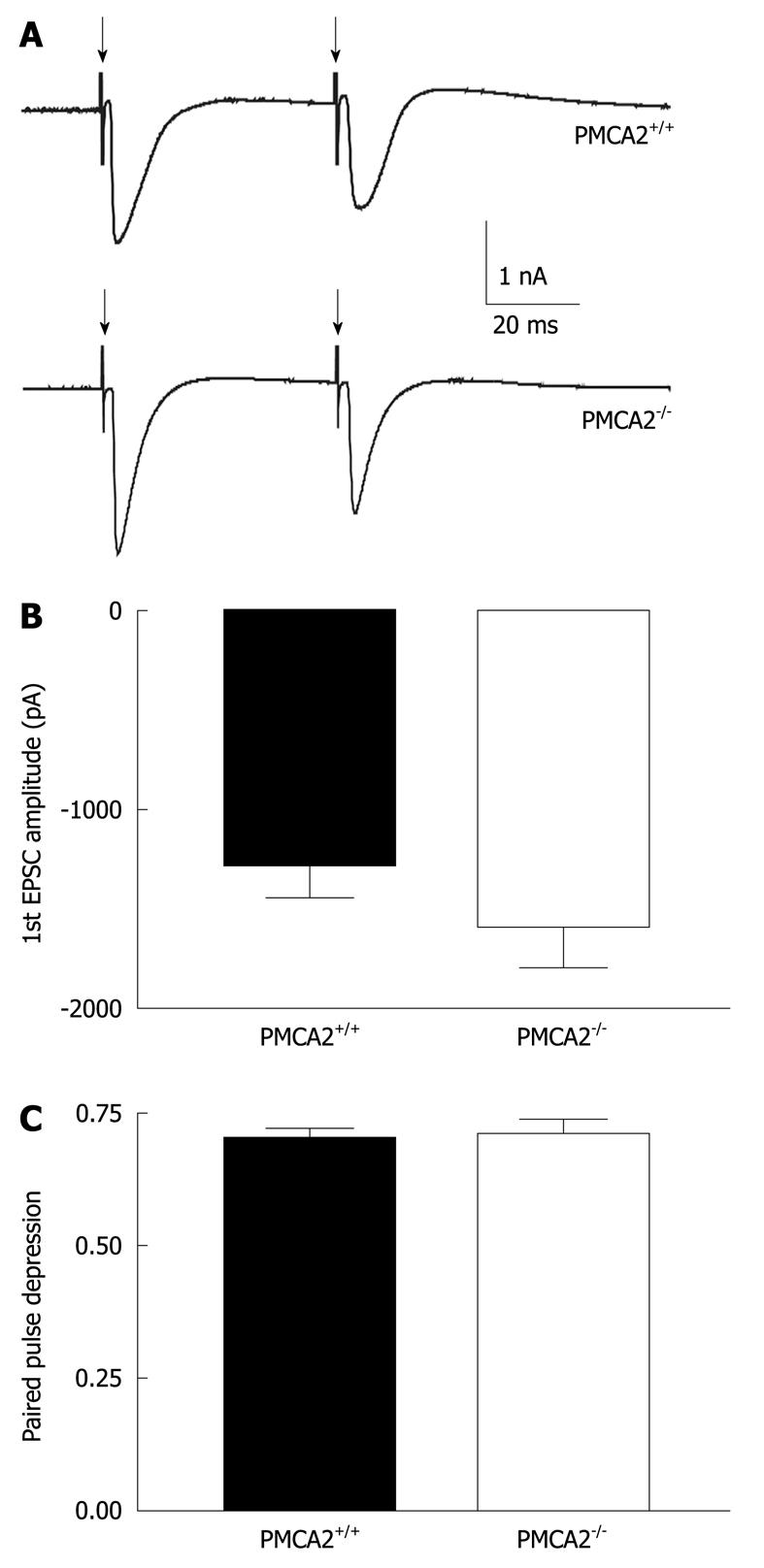
Figure 3 Intact CF evoked excitatory post-synaptic currents in PMCA2-/- PNs.
A: Representative traces of CF-evoked excitatory post-synaptic currents, EPSCs (stimulation shown by downward arrows) from individual mouse PNs voltage clamped at -20 mV. Patch electrodes contained 5mM QX314 to prevent the occurrence of Na+ dependent action potentials. Note that the second response, EPSC was smaller than the first, indicating a relative depression of the second EPSC (paired pulse depression) consistent with the high release probability of glutamate at the CF synapse[21]; B: There was no significant difference in the amplitude of the first EPSC; C: No significant difference in the extent of paired pulse depression. Values are mean ± SE error bars.
- Citation: Huang H, Nagaraja RY, Garside ML, Akemann W, Knöpfel T, Empson RM. Contribution of plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase to cerebellar synapse function. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(5): 95-102
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i5/95.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.95