Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2016; 7(20): 572-598
Published online Dec 15, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i20.572
Published online Dec 15, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i20.572
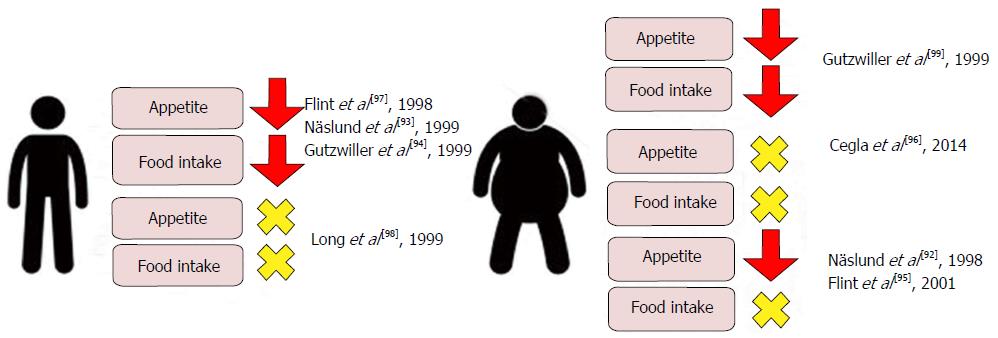
Figure 7 Effects on Visual Analogue Scale assessed appetite scores and ad libitum food intake in lean and obese subjects following physiological and supraphysiological[92-99] infusions of glucagon-like peptide 1.
Though individual studies report conflicting data, a meta-analysis of clinical studies evaluating the acute effects of GLP-1 infusion on food intake reports a mean 11.7% decrease when compared with saline control[100]. GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide 1.
- Citation: Anandhakrishnan A, Korbonits M. Glucagon-like peptide 1 in the pathophysiology and pharmacotherapy of clinical obesity. World J Diabetes 2016; 7(20): 572-598
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v7/i20/572.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i20.572