Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2015; 6(3): 500-507
Published online Apr 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i3.500
Published online Apr 15, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i3.500
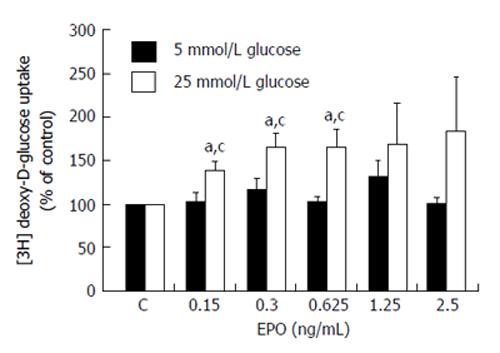
Figure 4 Effects of treatment with r-mo-erythropoietin on the rate of [3H]-deoxy-D-glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes cultured in either normal (5 mmol/L) or high (25 mmol/L) glucose medium (insulin: n = 8 and n = 6; r-mo-erythropoietin: n = 6 and n = 5, respectively).
aP < 0.05 vs control in the same medium; cP < 0.05 between the two media; Comparisons with control were performed using a one-sample t-test; pairwise comparisons between 5 and 25 mmol/L glucose-cultured cells were performed using a paired samples t-test. Republished with permission of Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart, New York from Mikolás et al[37]. EPO: Erythropoietin.
- Citation: Molnár GA, Mikolás EZ, Szijártó IA, Kun S, Sélley E, Wittmann I. Tyrosine isomers and hormonal signaling: A possible role for the hydroxyl free radical in insulin resistance. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(3): 500-507
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i3/500.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i3.500