Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Diabetes. Sep 10, 2015; 6(11): 1186-1197
Published online Sep 10, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i11.1186
Published online Sep 10, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i11.1186
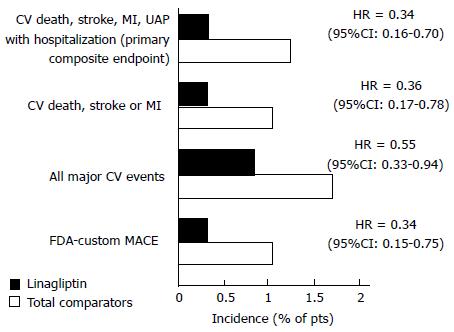
Figure 4 Cardiovascular tolerability profile of linagliptin in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Results of a pre-specified meta-analysis of eight randomized, double-blind trials in which patients treated with linagliptin 5 or 10 mg/d (n = 3159 and 160), glimepiride 1-4 mg/d (n = 781), voglibose 0.6 mg/d (n = 162) or placebo (n = 977) as monotherapy or in combination with other oral anti-hyperglycemia drugs for 18-52 wk[84]. It shows the incidence of primary and secondary composite endpoints in the linagliptin and total comparators group (primary analysis), together with corresponding hazard ratios and 95%CI. Adapted from Deeks[74]. CV: Cardiovascular; FDA: Food and Drug Administration; MACE: Major adverse CV events; MI: Myocardial infarction; pts: Patients; UAP: Unstable angina pectoris.
- Citation: Sanchez RA, Sanabria H, Santos CL, Ramirez AJ. Incretins and selective renal sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in hypertension and coronary heart disease. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(11): 1186-1197
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i11/1186.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i11.1186