Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2021; 13(6): 550-559
Published online Jun 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i6.550
Published online Jun 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i6.550
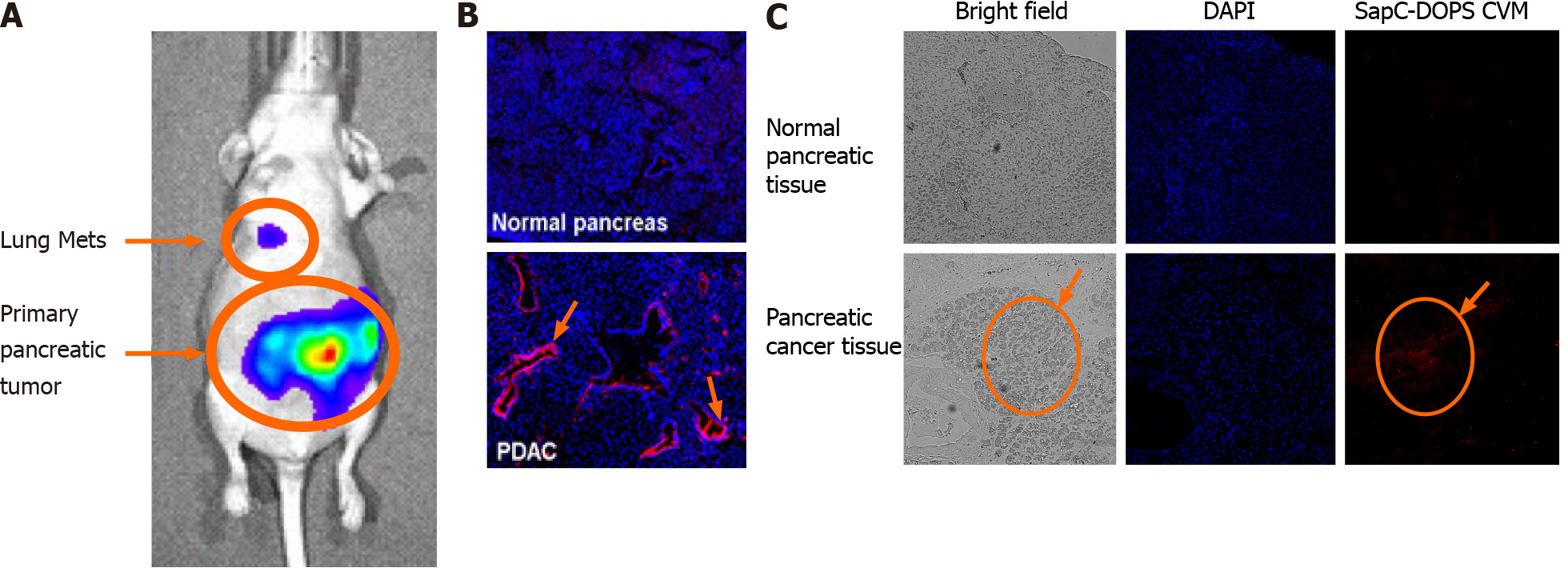
Figure 2 Saposin C-dioleoylphosphatidylserine targets pancreatic tumors.
Saposin C-dioleoylphosphatidylserine (SapC-DOPS) was fluorescently labeled with CellVue Maroon (CVM, a far red fluorescent probe) and injected into mice after pancreatic tumors were established from human cancer cells (cfPac-1-Luc3) (see details in reference 26)[26]. A: SapC-DOPS-CVM localized to the primary and lung metastatic tumors detected with intravascular ultrasound live animal imaging; B: Tumors, established from human MiaPaCa-2 cells, and normal pancreata of SapC-DOPS-CVM-injected mice were isolated and prepared for fluorescent microscopy. The slides, after staining with DAPI (blue) to detect nuclei, show accumulation of SapC-DOPS-CVM in the tumors. Note preferential SapC-DOPS labeling of ductal structures (arrows) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), and minimal binding to normal pancreas. SapC-DOPS is binding phosphatidylserine (PS) on the cancer cell surfaces as prior treatment with lactadherin, a PS binding protein, eliminates subsequent binding of SapC-DOPS; C: Frozen, unfixed sections from murine PDAC and matched normal pancreas tissues were incubated with SapC-DOPS-CVM nanovesicles for 20 min, counterstained with DAPI and mounted. The ovals localize the PDAC tumor. SapC-DOPS: Saposin C-dioleoylphosphatidylserine; CVM: CellVue Maroon; Mets: Metastatic tumors; PDAC: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
- Citation: Davis HW, Kaynak A, Vallabhapurapu SD, Qi X. Targeting of elevated cell surface phosphatidylserine with saposin C-dioleoylphosphatidylserine nanodrug as individual or combination therapy for pancreatic cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2021; 13(6): 550-559
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v13/i6/550.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v13.i6.550