Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2021; 13(5): 312-331
Published online May 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i5.312
Published online May 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i5.312
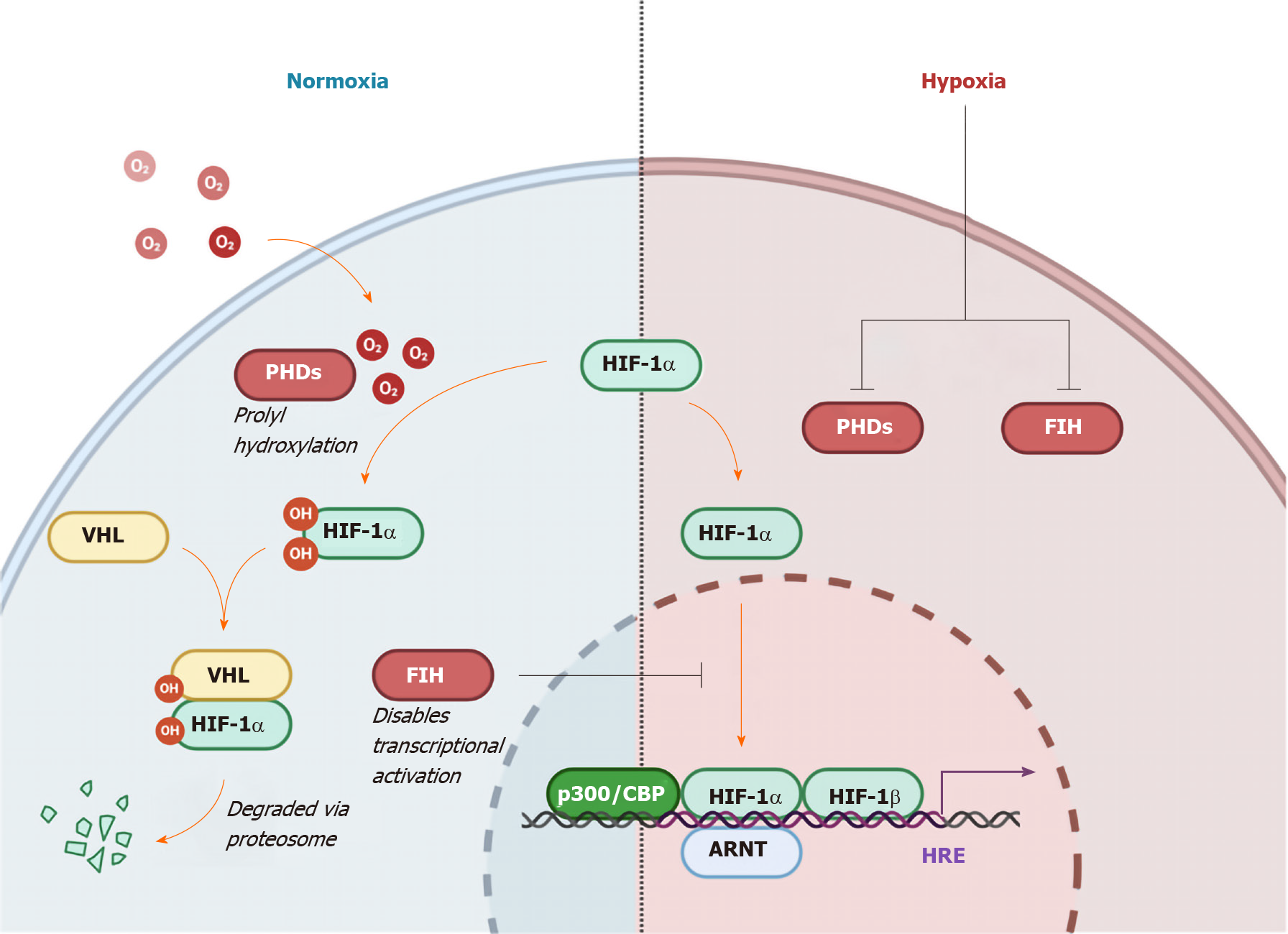
Figure 3 Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α by oxygen levels and von Hippel Lindau protein.
Hydroxylation by oxygen-dependent prolyl hydroxylase domain enzymes triggers recognition by the E3 ubiquitin ligase von Hippel Lindau, ensuring proteasomal degradation. In the non-von Hippel Lindau protein dependent pathway, induction of Factor Inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) leads to hydroxylation of an asparagine residue preventing HIF1-α from localizing with the co-activators p300 and CBP, hence disabling transcriptional activation[30]. The HIF pathway functions to conduct and orchestrate the cellular response to low oxygen availability[24,25]. HRE: Hypoxia response element; ARNT: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator; PHD: Prolyl hydroxylase domain enzymes; VHL: Von Hippel Lindau; HIF1-α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α; FIH: Factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor.
- Citation: King R, Hayes C, Donohoe CL, Dunne MR, Davern M, Donlon NE. Hypoxia and its impact on the tumour microenvironment of gastroesophageal cancers. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2021; 13(5): 312-331
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v13/i5/312.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v13.i5.312