Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Dec 16, 2021; 13(12): 673-697
Published online Dec 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i12.673
Published online Dec 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i12.673
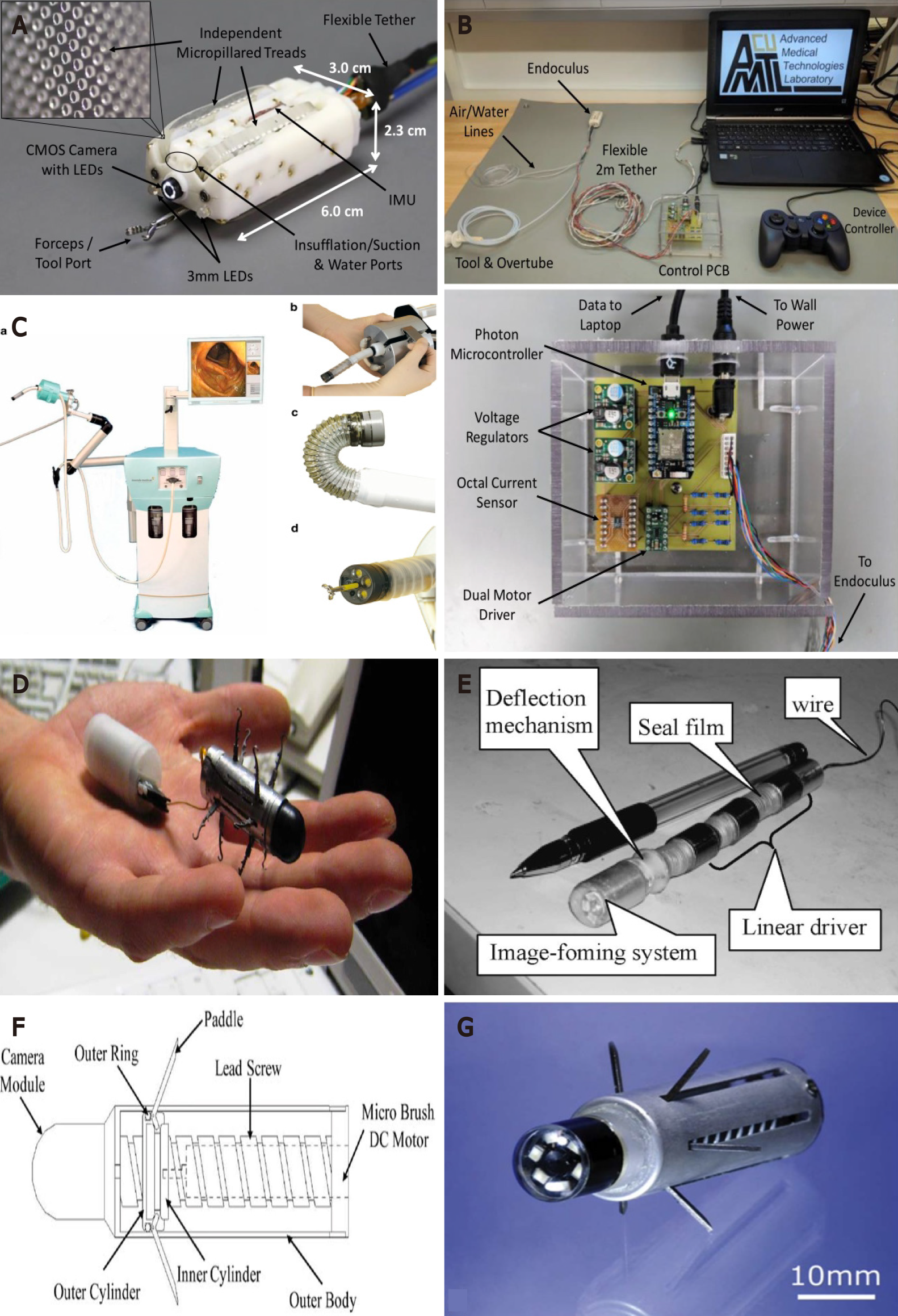
Figure 2 Examples of electromechanical robotic devices.
A: The treaded “Endonculus” tethered robot in isolation; B: The treaded “Endonculus” robot with its full operational set up and printed circuit board.Citation for A and B: Formosa GA, Prendergast JM, Edmundowicz SA, Rentschler ME. Novel Optimization-Based Design and Surgical Evaluation of a Treaded Robotic Capsule Colonoscope 2020; 36: 545-552. Copyright© The Authors 2020. Published by IEEE. C: The Invendoscope System with the tip in the driving motor, in full flexion and with a biopsy forceps in the working channel. Citation: Groth S, Rex DK, Rösch T, Hoepffner N. High cecal intubation rates with a new computer-assisted colonoscope: a feasibility study. Am J Gastroenterol 2011; 106: 1075-1080. Copyright© The Authors 2011. Published by American College of Gastroenterology. D: The six legged capsule device by Valdastri et al[25]. Citation: Valdastri P, Webster RJ, Quaglia C, Quirini M, Menciassi A Dario P. A New Mechanism for Mesoscale Legged Locomotion in Compliant Tubular Environments. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2009; 25: 1047-1057. Copyright© The Authors 2009. Published by IEEE. E: A worm-like endoscope prototype. Citation: Wang K, Yan G. Micro robot prototype for colonoscopy and in vitro experiments. J Med Eng Technol 2007; 31: 24-28. Copyright© The Authors 2007. Published by Taylor & Francis Ltd. F: Cross-sectional paddled capsular device; G: Complete paddled capsular device. Citation for F and G: Kim HM, Yang S, Kim J, Park S, Cho JH, Park JY, Kim TS, Yoon ES, Song SY, Bang S. Active locomotion of a paddling-based capsule endoscope in an in vitro and in vivo experiment (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 72: 381-387. Copyright© The Authors 2010. Published by Elsevier.
- Citation: Sekhon Inderjit Singh HK, Armstrong ER, Shah S, Mirnezami R. Application of robotic technologies in lower gastrointestinal tract endoscopy: A systematic review. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2021; 13(12): 673-697
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v13/i12/673.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v13.i12.673