Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Hepatol. Jan 28, 2017; 9(3): 131-138
Published online Jan 28, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i3.131
Published online Jan 28, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i3.131
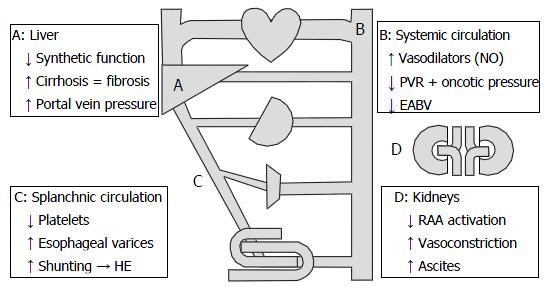
Figure 2 Systemic effects of cirrhosis.
Increased portal vein pressure results in vasodilation decreasing peripheral vascular resistance (PVR) and effective arterial blood volume (EABV). To compensate for this, increased renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) activation leads to sodium and fluid retention along with renal vasoconstriction and reduced glomerular filtration rate. Adopted with permission from Ho et al[27]. HE: Hepatic encephalopathy.
- Citation: Scappaticci GB, Regal RE. Cockcroft-Gault revisited: New de-liver-ance on recommendations for use in cirrhosis. World J Hepatol 2017; 9(3): 131-138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v9/i3/131.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v9.i3.131