Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Aug 18, 2016; 8(23): 985-993
Published online Aug 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i23.985
Published online Aug 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i23.985
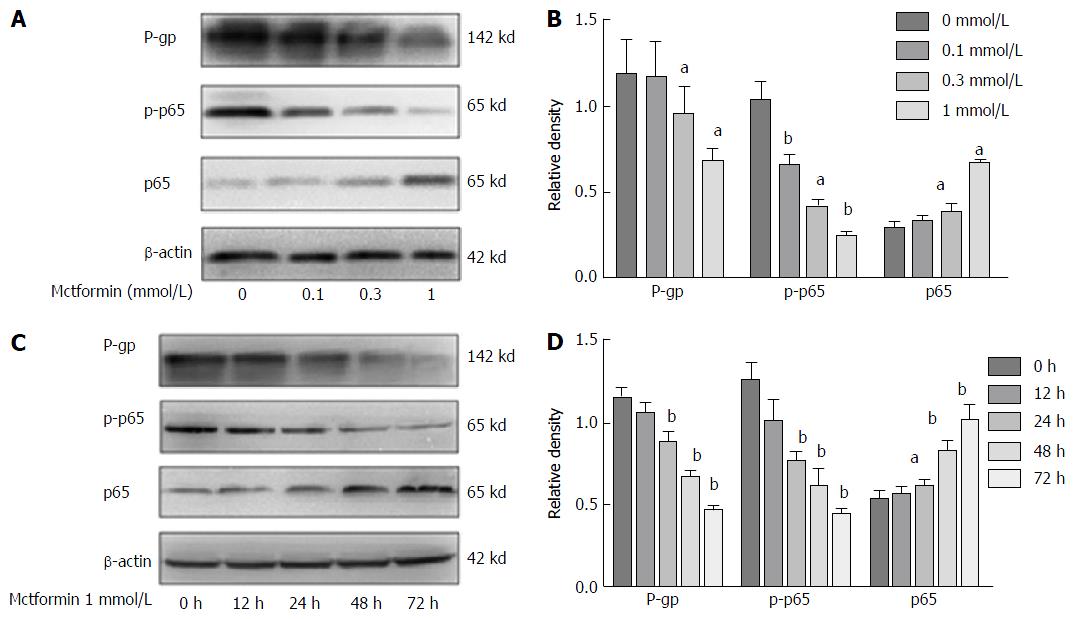
Figure 3 Metformin down-regulates P-glycoprotein expression via the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway.
A: After HepG2/ADM cells were treated with different doses of metformin for 24 h, the levels of P-gp and p-p65 expression analyzed by Western blot were decreased in a dose-dependent manner, and the cytoplasma p65 increased in a dose-dependent manner; B: The gray intensity images of Figure 3A. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the blank group (n = 3, mean ± SD); C: After HepG2/ADM cells were treated with 1 mmol/L metformin for different time periods, the levels of P-gp and p-p65 expression analyzed by Western blot were decreased in a time-dependent manner, and the cytoplasma p65 increased in a time-dependent manner; D: The gray intensity images of Figure 3C. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the blank group (n = 3, mean ± SD). P-gp: P-glycoprotein; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; ADM: Adriamycin.
- Citation: Wu W, Yang JL, Wang YL, Wang H, Yao M, Wang L, Gu JJ, Cai Y, Shi Y, Yao DF. Reversal of multidrug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by metformin through inhibiting NF-κB gene transcription. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(23): 985-993
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i23/985.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i23.985