Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Jul 18, 2016; 8(20): 858-862
Published online Jul 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i20.858
Published online Jul 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i20.858
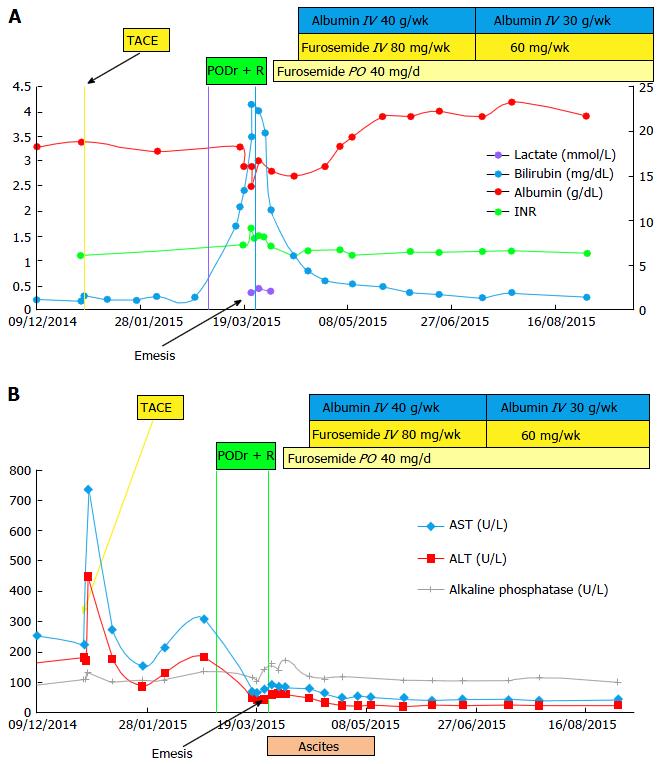
Figure 1 Change in laboratories in relation to antiviral therapy (A) and in aminotransferase and Alkaline Phosphate levels over time (B).
A: Change in laboratories in relation to antiviral therapy. Shortly after initiation of hepatitis C treatment, and after 4 mo of stable levels, laboratory values deteriorated indicating a decline in hepatic synthetic function; peak bilirubin - 23 mg/dL, PT/INR - 1.65, lactate-2.44 mg/dL, lowest albumin - 2.5 g/L. Shortly after treatment discontinuation, laboratory values slowly returned to baseline; B: Change in aminotransferase and alkaline phosphate levels over time. There was a spike in aminotransferase levels after the TACE procedure. Following HCV treatment initiation, aminotransferase levels declined over time, reaching plateau levels of AST = 40 U/L and ALT = 25 U/L. Aminotransferase levels remained stable when total bilirubin and PT/INR levels increased (shown in Figure 1A above). AST: Aspartate transaminase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; TACE: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; INR: International normalized ratio; PODr + R: Paritaprevir, Ombitasvir, Dasabuvir, Ritonavir, and Ribavirin; IV: Intravenous; PO: By mouth.
- Citation: Hasin Y, Shteingart S, Dahari H, Gafanovich I, Floru S, Braun M, Shlomai A, Verstandig A, Dery I, Uprichard SL, Cotler SJ, Lurie Y. Hepatitis C virus cures after direct acting antiviral-related drug-induced liver injury: Case report. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(20): 858-862
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i20/858.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i20.858