Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Nov 18, 2015; 7(26): 2664-2675
Published online Nov 18, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i26.2664
Published online Nov 18, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i26.2664
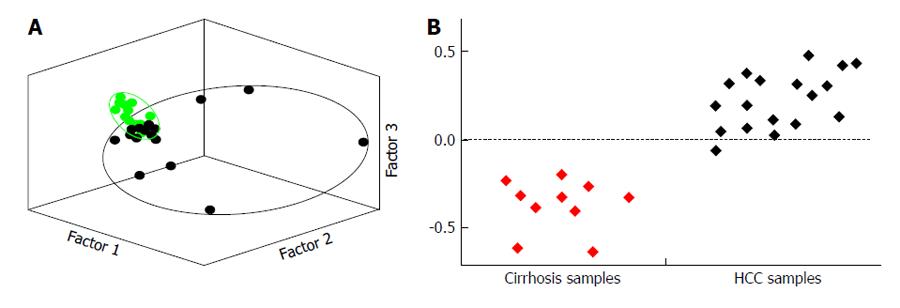
Figure 5 Principal components multivariate statistical analysis (A) and partial least squared discriminant multivariate statistical analysis (B).
A: Principal components multivariate statistical analysis scatter plot showing statistical separation of data sets of urinary nuclear magnetic (NMR) spectroscopy information of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) subjects (small black spots), compared to urinary data sets from healthy controls (small green spots); B: Partial least squared discriminant multivariate statistical analysis showing statistical differentiation of metabolite information from HCC subjects obtained using NMR spectroscopy, compared to similar urinary data sets from patients with cirrhosis. These are the essential raisons d’être for searching and using urinary biomarkers for the early and reliable diagnosis of HCC, but promising research is still being undertaken to this end (Figure 6).
- Citation: Trovato FM, Tognarelli JM, Crossey MM, Catalano D, Taylor-Robinson SD, Trovato GM. Challenges of liver cancer: Future emerging tools in imaging and urinary biomarkers. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(26): 2664-2675
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i26/2664.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i26.2664