Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Jul 8, 2015; 7(13): 1735-1741
Published online Jul 8, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i13.1735
Published online Jul 8, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i13.1735
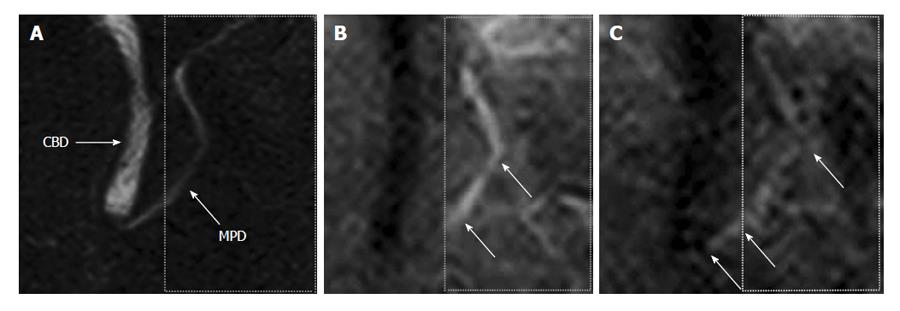
Figure 3 A 47-year-old male with normal volunteer.
A: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography image. Labelling pulse of pancreas juice is applying to box surrounded by dotted lines on pancreas juice in body and caudal portion of the 3) main pancreatic duct; B: Time-SLIP image is not showing movement of pancreatic juice; C: Flow of pancreatic juice from body of the pancreas into head of pancreas is noted by high signal intensity (arrows). Reprinted from Sugita et al[43] (by permission of Wiley Periodicals, Inc). CBD: Common bile duct; MPD: Main pancreatic duct.
- Citation: Sugita R. Pancreaticobiliary reflux as a high-risk factor for biliary malignancy: Clinical features and diagnostic advancements. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(13): 1735-1741
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i13/1735.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i13.1735