Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Hepatol. Aug 27, 2014; 6(8): 580-595
Published online Aug 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i8.580
Published online Aug 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i8.580
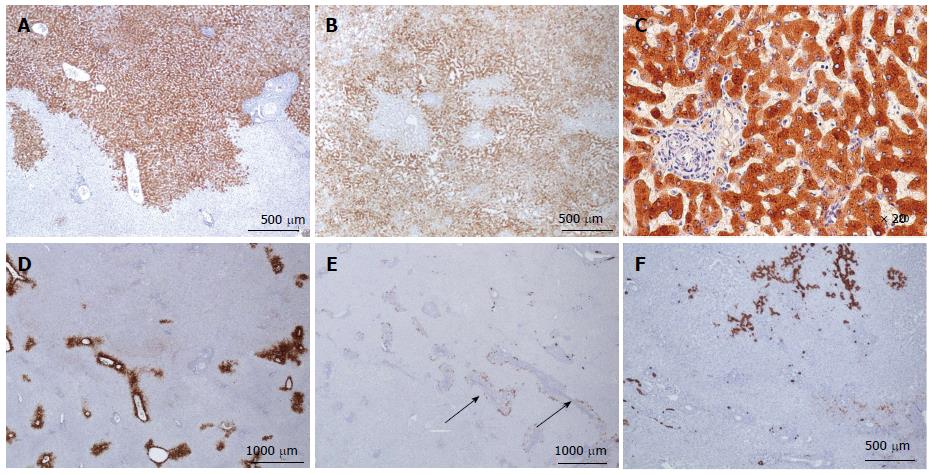
Figure 12 Inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma immunohistochemistry.
A, B: Same patient as Figure 10 F, different tumors. C-reactive protein (CRP): typical aspect of inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma (IHCA) with strong and diffuse expression in tumoral hepatocytes, with sharp demarcation from the surrounding non tumoral liver (A); more irregular CRP staining with limited areas remaining negative (B); C: Same patient as Figure 10D. CRP is expressed only in hepatocytes. D, E: Same patient as Figure 10F. D: Glutamine synthase: no abnormal staining; positivity only in some perivenous hepatocytes at the periphery of the nodule. E: CK7: faint staining around pseudo portal tracts, underlining ductular reaction, a common finding in IHCA. F: Same patient as Figure 10A. CK7 highlights the major ductular reaction at the periphery of pseudo portal tracts.
- Citation: Sempoux C, Balabaud C, Bioulac-Sage P. Pictures of focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatocellular adenomas. World J Hepatol 2014; 6(8): 580-595
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v6/i8/580.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i8.580