Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Hepatol. Aug 27, 2014; 6(8): 549-558
Published online Aug 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i8.549
Published online Aug 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i8.549
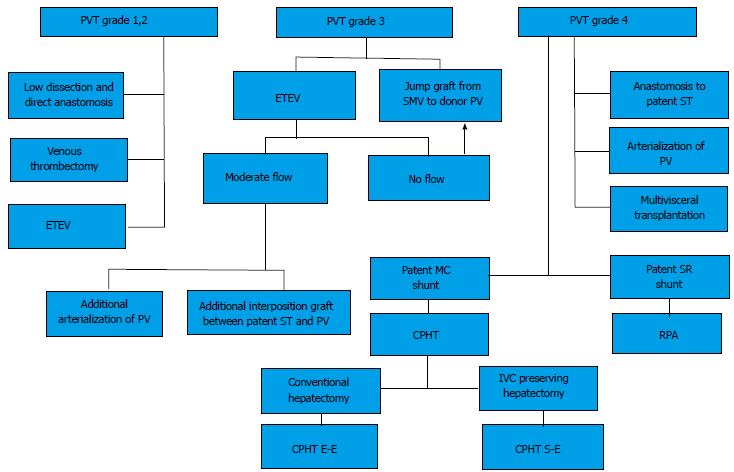
Figure 2 Algorithm for the management of portal and splanchnic vein thrombosis during liver transplantation.
CPHT: Cavo-portal hemitransposition; CPHT E-E: End-to-end cavo-portal hemitransposition; CPHT S-E: Side-to-end cavo-portal hemitransposition; ETEV: Eversion thromboendovenectomy; IVC: Inferior vena cava; MC: Mesocaval shunt (spontaneous or surgical); PV: Portal vein; PVT: Portal vein thrombosis; RPA: Reno-portal anastomosis; SMV: Superior mesenteric vein; SR: Splenorenal shunt (spontaneous or surgical); ST: Splanchnic tributary (coronary, gastroepiploic vein). From Paskonis et al[43], with modifications.
- Citation: Lai Q, Spoletini G, Pinheiro RS, Melandro F, Guglielmo N, Lerut J. From portal to splanchnic venous thrombosis: What surgeons should bear in mind. World J Hepatol 2014; 6(8): 549-558
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v6/i8/549.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i8.549