Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2010; 2(12): 419-427
Published online Dec 27, 2010. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i12.419
Published online Dec 27, 2010. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i12.419
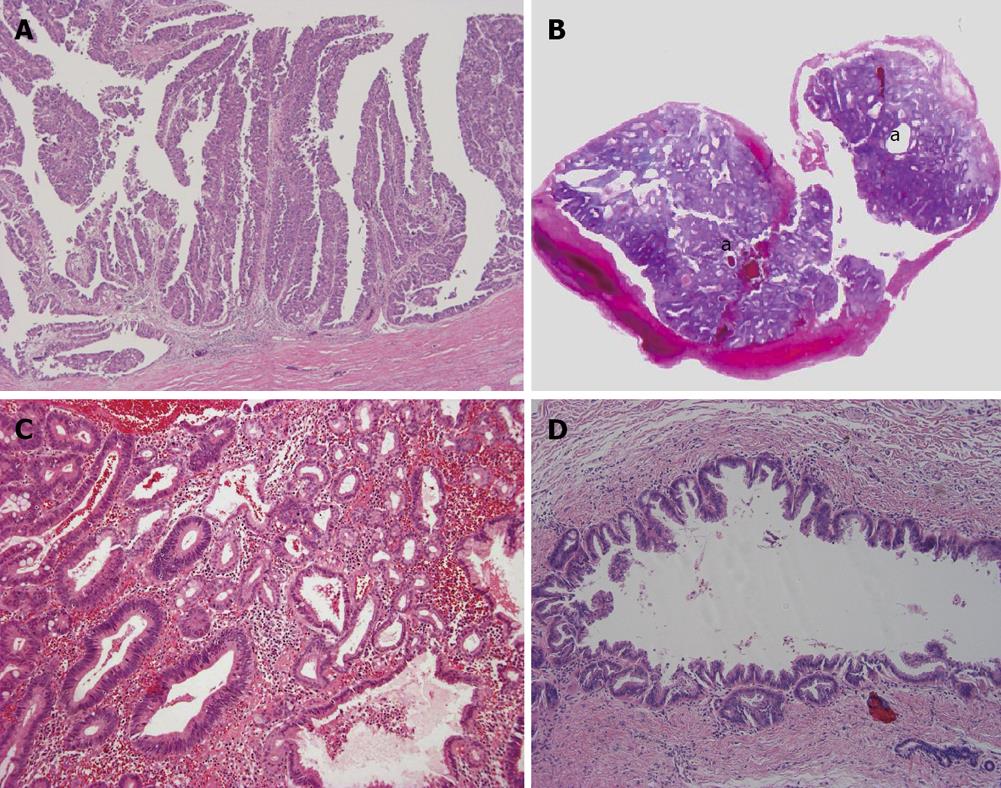
Figure 4 Intraductal type of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
A: Intraductal papillary neoplasm of bile duct. Neoplastic biliary epithelia show papillary growth in the dilated lumen. There is no invasion into the duct wall; B: Intraductal tubular neoplasm of bile duct. The neoplasm (a) appears as a cast in the dilated lumen; C: Intraductal tubular neoplasm of bile duct. The tubular pattern is predominant. Higher magnification of Figure 4B; D: Superficial spreading type. Carcinoma cells show intraductal, intraepithelial growth with a micropapillary configuration and intraglandular involvement. There is no evident invasion into the duct wall.
- Citation: Nakanuma Y, Sato Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, Xu J, Ikeda H. Pathological classification of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma based on a new concept. World J Hepatol 2010; 2(12): 419-427
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v2/i12/419.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v2.i12.419