Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2025; 17(3): 103854
Published online Mar 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.103854
Published online Mar 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.103854
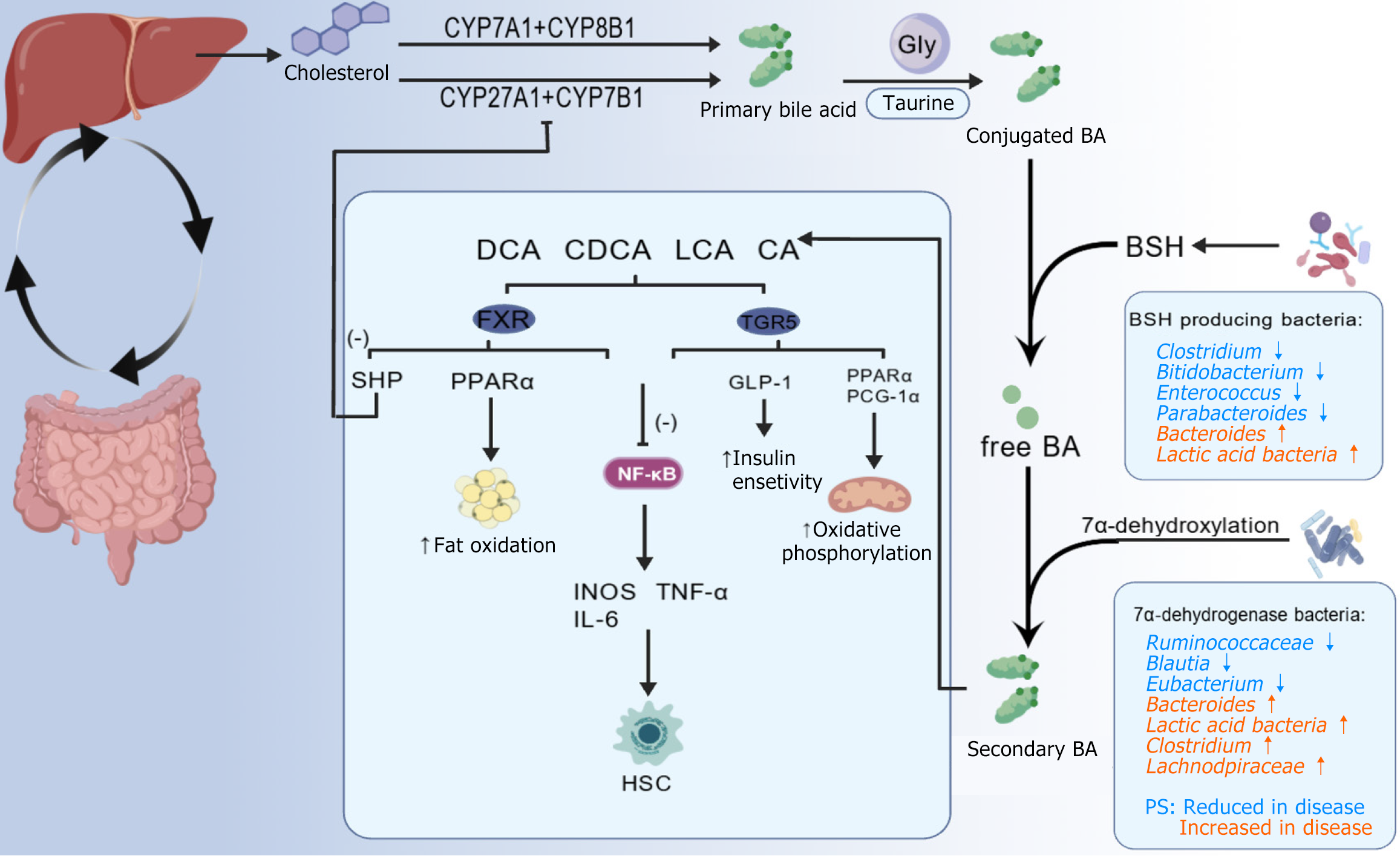
Figure 3 In the enterohepatic circulation, cholesterol within the liver is metabolized into bile acids via two distinct pathways.
Influenced by the gut microbiota, primary bile acids are further transformed into secondary bile acids, which include cholic acid (CA), chenodeoxycholic acid, lithocholic acid, and cholic acid. These secondary bile acids can activate the farnesoid X receptor and TGR5 receptor, thereby exerting a disease - alleviating effect. DCA: Deoxycholic acid; CDCA: Chenodeoxycholic acid; LCA: Lithocholic acid; CA: Cholic acid; BA: Bile acid; BSH: Bile salt hydrolase; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell. Created from BIOGDP.com[93].
- Citation: Shu JZ, Huang YH, He XH, Liu FY, Liang QQ, Yong XT, Xie YF. Gut microbiota differences, metabolite changes, and disease intervention during metabolic - dysfunction - related fatty liver progression. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(3): 103854
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i3/103854.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.103854