Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2023; 15(11): 1196-1209
Published online Nov 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i11.1196
Published online Nov 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i11.1196
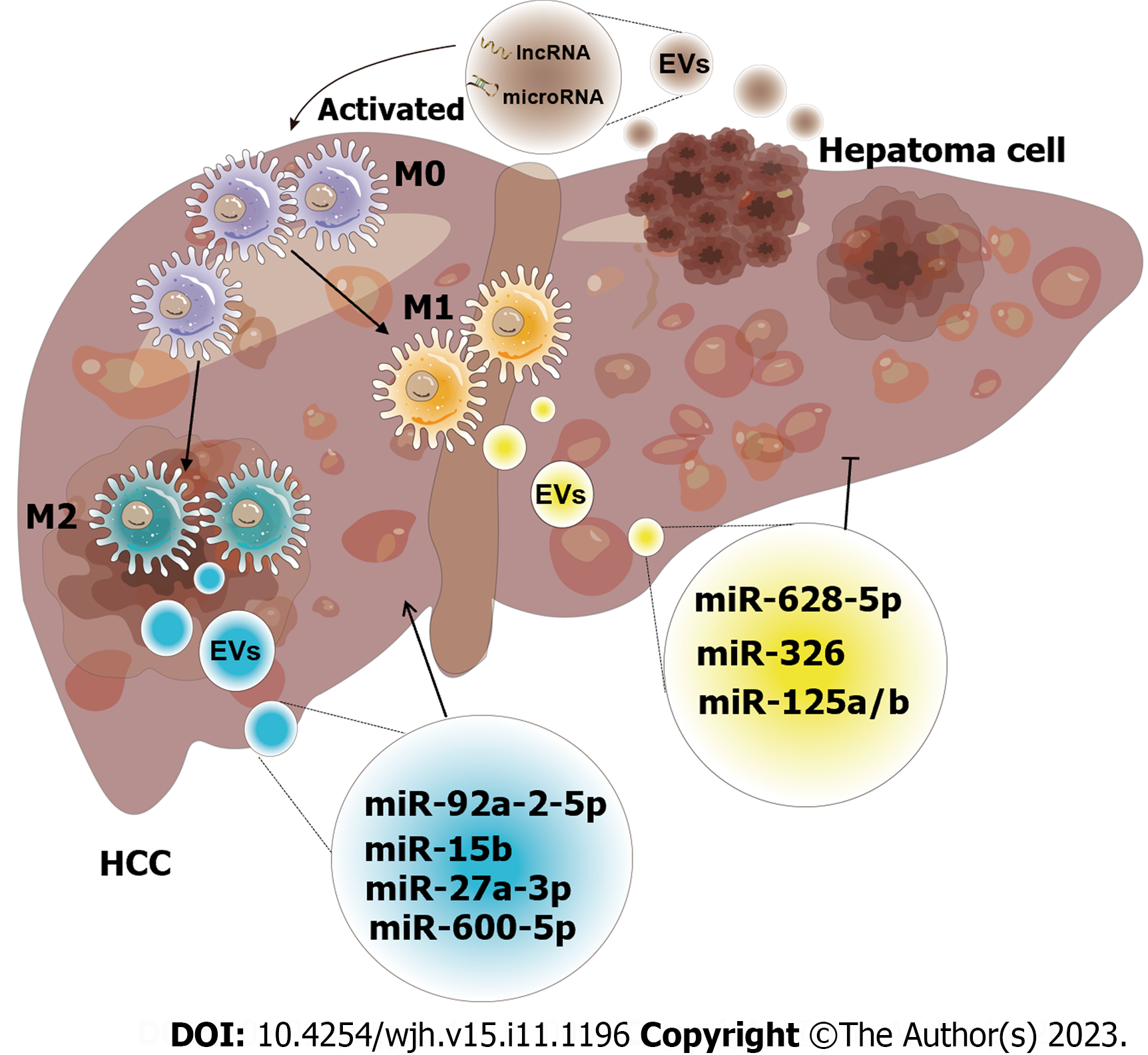
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of the effect of exosomes derived from macrophages on hepatocellular carcinoma.
The crosstalk of exosomes between macrophages and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) affects tumor progression. Both exosomes released by macrophages and HCC have unique intracellular components, including a variety of mRNAs, microRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, lipids, etc. These intracellular components are utilized as communicators to induce pathways that result in increased or inhibited cell proliferation, invasion, and other hallmarks of malignancy (M0: M0 macrophage; M1: M1 macrophage; M2: M2 macrophage; miR-92a-2-5p[82]; miR-15b[83]; miR-27a-3p[85]; miR-660-5p[86]; miR-628-5p[87]; miR-326[88]; miR-125a/b[90]). EVs: Extracellular vesicles; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; miRNA: MicroRNA; lncRNA: Long non-coding RNA.
- Citation: Xiang SY, Deng KL, Yang DX, Yang P, Zhou YP. Function of macrophage-derived exosomes in chronic liver disease: From pathogenesis to treatment. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(11): 1196-1209
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i11/1196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i11.1196