Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2017; 9(3): 45-67
Published online Mar 26, 2017. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v9.i3.45
Published online Mar 26, 2017. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v9.i3.45
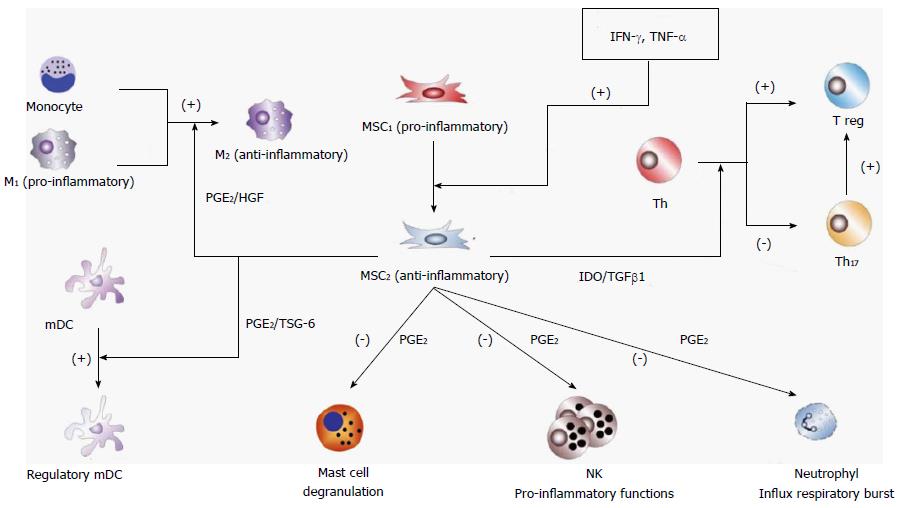
Figure 1 Mesenchymal stem cell immunosuppressive regulatory effects.
MSCs are polarized to an immunosuppressive stage (MSC2) by a high relative concentration of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ and TNF-α. MSC2 induce macrophage polarization of monocytes and pro-inflammatory macrophages (M1) to the immunosuppressive stage M2 by secreting immunomodulatory mediators such as PGE2 and HGF. MSC2 also induce differentiation of Th and Th17 to T regulatory cells (Treg) by secretion of TGF-β1 and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). Furthermore, MSC2 induce differentiation of mDCs to a regulatory anti-inflammatory stage (mDCreg), inhibit mast cell degranulation, inhibit NK cell pro-inflammatory functions and suppresses neutrophil respiratory burst. MSC2-derived PGE2 contributes to all of these effects. Other cytokines that have been implicated in at least some of the MSC2 immune-suppressive effects are IL-6 and GM-CSF[8]. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; Th: T helper; HGF: Hepatic growth factor; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-beta 1; mDCs: Monocyte-derived dendritic cells; NK: Natural killer; IL-6: Interleukin-6; GM-CSF: Granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor.
- Citation: Zorzopulos J, Opal SM, Hernando-Insúa A, Rodriguez JM, Elías F, Fló J, López RA, Chasseing NA, Lux-Lantos VA, Coronel MF, Franco R, Montaner AD, Horn DL. Immunomodulatory oligonucleotide IMT504: Effects on mesenchymal stem cells as a first-in-class immunoprotective/immunoregenerative therapy. World J Stem Cells 2017; 9(3): 45-67
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v9/i3/45.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v9.i3.45